Cellular localization and allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin protein by peptide nucleic acid oligomers containing the fluorescent nucleobase [bis-o-(aminoethoxy)phenyl]pyrrolocytosine
- PMID: 19783436
- PMCID: PMC2770837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.09.004
Cellular localization and allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin protein by peptide nucleic acid oligomers containing the fluorescent nucleobase [bis-o-(aminoethoxy)phenyl]pyrrolocytosine
Abstract
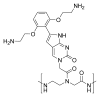
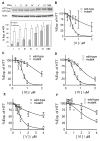
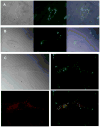
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a successful DNA/RNA mimic. A major challenge for research is to invent chemically modified PNAs that retain the favorable properties of the parent compound while improving biological recognition. Here, we test modified PNAs containing [bis-o-(aminoethoxy)phenyl]pyrrolocytosine bases designed to engage guanine with an additional hydrogen bond. We observe elevated melting temperatures, localization to cellular compartments, and allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin protein expression.
Figures
References
-
- Nielsen PE. Mol Biotech. 2004;26:233. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen PE, Egholm M, Berg RH, Buchardt O. Science. 1991;254:1497. - PubMed
-
- Egholm M, Buchardt O, Christensen L, Behrens C, Freier SM, Driver DA, Berg RH, Kim SK, Norden B, Nielsen PE. Nature. 1993;365:566. - PubMed
-
- Smulevitch SV, Simmons CG, Norton JC, Wise TW, Corey DR. Nat Biotech. 1996;14:1700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

