Inhibition of KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphomas in NOD/SCID mice by gamma-secretase inhibitor
- PMID: 19783901
- PMCID: PMC5965683
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.22.9743
Inhibition of KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphomas in NOD/SCID mice by gamma-secretase inhibitor
Erratum in
-
Correction.Cancer Biol Ther. 2021 Jun 3;22(5-6):414. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.1926127. Epub 2021 May 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34039251 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a common cancer in AIDS patients closely associated with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). Previously, we showed that KSHV latency associated nuclear antigen (LANA) stabilizes intracellular activated Notch1 (ICN) involved in maintenance of the malignant phenotype of KSHV infected PEL cells in vitro. The gamma-secretase inhibitor (GSI) which specifically blocks the production of ICN slows down the proliferation of the KSHV infected PEL cell lines BCBL1, BC3 as well as JSC1 in vitro. In this study, we extended these studies to explore the possibility that manipulation of the Notch signaling by GSI would prevent the growth of the PEL tumors in vivo. We observed that the onset of tumorigenesis of KSHV infected PELs was significantly delayed in GSI treated SCID mice harboring the PEL cell lines. We also found that GSI treatment resulted in necrosis as well as apoptosis in tumors generated by the xenotransplanted KSHV positive PEL cell lines. In contrast, GSI had no effect on mice harboring BJAB cells, a KSHV negative Burkitt's lymphoma cell line where ICN levels were negligible. Our study provides further evidence to suggest that targeted downregulation of abnormal Notch signaling has therapeutic potential for KSHV related primary effusion lymphomas.
Figures

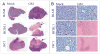
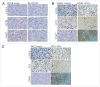

Comment in
-
Gamma-secretase inhibitors--do they have a role in the treatment of B cell lymphoma?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Nov;8(22):2144-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.22.10034. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 20068386 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boshoff C, Whitby D, Talbot S, Weiss RA. Etiology of AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma and lymphoma. Oral Dis. 1997;3:129–32. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, Moore PS. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
