Identification of a benzamide derivative that inhibits stress-induced adrenal corticosteroid synthesis
- PMID: 19783933
- PMCID: PMC6254727
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules14093392
Identification of a benzamide derivative that inhibits stress-induced adrenal corticosteroid synthesis
Abstract
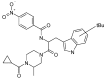
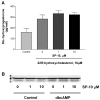
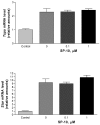
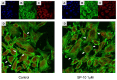
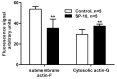
Elevated serum glucocorticoid levels contribute to the progression of many diseases, including depression, Alzheimer's disease, hypertension, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Here we show that the benzamide derivative N-[2-(4-cyclopropanecarbonyl-3-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-1-(tert-butyl-1H-indol-3-yl-methyl)-2-oxo-ethyl]-4-nitrobenzamide (SP-10) inhibits dibutyryl cyclic AMP (dbcAMP)-induced corticosteroid synthesis in a dose-dependent manner in Y-1 adrenal cortical mouse tumor cells, without affecting basal steroid synthesis and reduced stress-induced corticosterone increases in rats without affecting the physiological levels of the steroid in blood. SP-10 did not affect cholesterol transport and metabolism by the mitochondria but was unexpectedly found to increase 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A, low density lipoprotein receptor, and scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) expression. However, it also markedly reduced dbcAMP-induced NBD-cholesterol uptake, suggesting that this is a compensatory mechanism aimed at maintaining cholesterol levels. SP-10 also induced a redistribution of filamentous (F-) and monomeric (G-) actin, leading to decreased actin levels in the submembrane cytoskeleton suggesting that SP-10-induced changes in actin distribution might prevent the formation of microvilli-cellular structures required for SRBI-mediated cholesterol uptake in adrenal cells.
Figures





References
-
- Kiraly S.J., Ancill R.J., Dimitrova G. The relationship of endogenous cortisol to psychiatric disorder: a review. Can. J. Psychiatry. 1997;42:415–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

