Interactions between PD-1 and PD-L1 promote tolerance by blocking the TCR-induced stop signal
- PMID: 19783989
- PMCID: PMC2778301
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1790
Interactions between PD-1 and PD-L1 promote tolerance by blocking the TCR-induced stop signal
Abstract
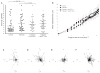
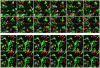
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) is an inhibitory molecule expressed on activated T cells; however, the biological context in which PD-1 controls T cell tolerance remains unclear. Using two-photon laser-scanning microscopy, we show here that unlike naive or activated islet antigen-specific T cells, tolerized islet antigen-specific T cells moved freely and did not swarm around antigen-bearing dendritic cells (DCs) in pancreatic lymph nodes. Inhibition of T cell antigen receptor (TCR)-driven stop signals depended on continued interactions between PD-1 and its ligand, PD-L1, as antibody blockade of PD-1 or PD-L1 resulted in lower T cell motility, enhanced T cell-DC contacts and caused autoimmune diabetes. Blockade of the immunomodulatory receptor CTLA-4 did not alter T cell motility or abrogate tolerance. Thus, PD-1-PD-L1 interactions maintain peripheral tolerance by mechanisms fundamentally distinct from those of CTLA-4.
Figures




Comment in
-
Making antigen invisible: a coinhibitory molecule regulates the interaction between T cells and dendritic cells.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010 Mar;9(3):243-7. doi: 10.1586/erv.09.164. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010. PMID: 20218851
References
-
- Walunas TL, et al. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–13. - PubMed
-
- Tivol EA, et al. Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity. 1995;3:541–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

