Hemodynamics of Cerebral Aneurysms
- PMID: 19784385
- PMCID: PMC2750901
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.40.111406.102126
Hemodynamics of Cerebral Aneurysms
Abstract
The initiation and progression of cerebral aneurysms are degenerative processes of the arterial wall driven by a complex interaction of biological and hemodynamic factors. Endothelial cells on the artery wall respond physiologically to blood-flow patterns. In normal conditions, these responses are associated with nonpathological tissue remodeling and adaptation. The combination of abnormal blood patterns and genetics predisposition could lead to the pathological formation of aneurysms. Here, we review recent progress on the basic mechanisms of aneurysm formation and evolution, with a focus on the role of hemodynamic patterns.
Figures


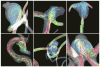
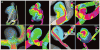
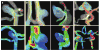

References
-
- Alastruey J, Parker KH, Peiro J, Byrd SM, Sherwin SJ. Modelling the circle of Willis to assess the effects of anatomical variations and occlusions on cerebral flows. J Biomech. 2007;40:1794–805. - PubMed
-
- Alnaes MS, Isaksen J, Mardal KE, Rommer B, Morgan MK, Ingebritsen T. Computation of hemodynamics in the circle of Willis. Stroke. 2007;38:2500–5. - PubMed
-
- Basombrio F, Dari E, Buscaglia GC, Feijoo RA. Numerical experiments in complex haemodynamics flows: non-Newtonian effects. Presented at XI ENIEF; Bariloche, Argentina. 2000.
-
- Black SPW, German WL. Observation on the relationship between the volume and the size of the orifice of experimental aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1960;17:984–90. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
