Effects of inactivation-resistant agonists on the signalling, desensitization and down-regulation of bradykinin B(2) receptors
- PMID: 19785654
- PMCID: PMC2782347
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00409.x
Effects of inactivation-resistant agonists on the signalling, desensitization and down-regulation of bradykinin B(2) receptors
Abstract
Background and purpose: A peptide bradykinin (BK) B(2) receptor agonist partially resistant to degradation, B-9972, down-regulates this receptor subtype. We have used another recently described non-peptide agonist, compound 47a, as a tool to study further the effects of metabolically more stable and thus persistent, agonists of the BK B(2) receptor on signalling, desensitization and down-regulation of this receptor.
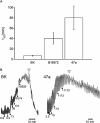
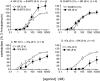
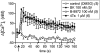
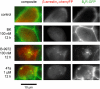
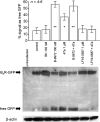
Experimental approach and key results: Compound 47a was a partial agonist at the B(2) receptor in the human umbilical vein, where it shared with B-9972 a very slow relaxation on washout, and in HEK 293 cell lines expressing tagged forms [myc, green fluorescent protein (GFP)] of the rabbit B(2) receptor. Compound 47a desensitized the umbilical vein to BK. In the cellular systems, the inactivation-resistant agonists induced [Ca(2+)](i) transients as brief as those of BK but affected other functions with a longer duration than BK [12 h; receptor endocytosis, endosomal beta-arrestin(1/2) translocation, protein kinase C-dependent extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK)1/2 phosphorylation and c-Fos expression]. The B(2) receptor-GFP was degraded in cells exposed to B-9972 or compound 47a for 12 h. The non-peptide B(2) receptor antagonist LF 16-0687 prevented all effects of compound 47a, which were also absent in cells lacking recombinant B(2) receptors.
Conclusion and implications: Inactivation-resistant agonists revealed a long-lasting assembly of the agonist-B(2) receptor-beta-arrestin complexes in endosomal structures and induce 'biased signalling' (in terms of activation of ERK and c-Fos) as a function of time. Further, B-9972 and compound 47a, unlike BK, efficiently down-regulated BK B(2) receptors.
Figures
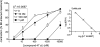





Similar articles
-
B-9972 (D-Arg-[Hyp3,Igl5,Oic7,Igl8]-bradykinin) is an inactivation-resistant agonist of the bradykinin B2 receptor derived from the peptide antagonist B-9430 (D-Arg-[Hyp3,Igl5,D-Igl7,Oic8]-bradykinin): pharmacologic profile and effective induction of receptor degradation.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Nov;323(2):534-46. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.123422. Epub 2007 Aug 15. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17699739
-
Prolonged signalling and trafficking of the bradykinin B2 receptor stimulated with the amphibian peptide maximakinin: insight into the endosomal inactivation of kinins.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Feb;65(2):247-53. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22108573
-
Pharmacological characterisation of the first non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor agonist FR 190997: an in vitro study on human, rabbit and pig vascular B2 receptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999 Oct;360(4):361-7. doi: 10.1007/s002109900087. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10551272
-
Vasopeptidase-activated latent ligands of the histamine receptor-1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):677-83. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24016859
-
Bradykinin receptor types and B2 subtypes.Life Sci. 1994;55(10):735-49. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00557-5. Life Sci. 1994. PMID: 8072371 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of bradykinin receptor type 2 in spontaneous extravasation in mice skin: implications for non-allergic angio-oedema.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 May;175(10):1607-1620. doi: 10.1111/bph.14166. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29465763 Free PMC article.
-
Binding characteristics of [3H]-JSM10292: a new cell membrane-permeant non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;167(4):839-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02054.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22646218 Free PMC article.
-
G-protein coupled receptor resensitization-appreciating the balancing act of receptor function.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 May 30. Online ahead of print. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22697395 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Pathways of Bradykinin Formation in Whole Blood From Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Hereditary Angioedema Due to C1 Inhibitor Deficiency.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 2;9:2183. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02183. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30333824 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Pharmacological Profile of a New Small Molecule Bradykinin B2 Receptor Antagonist.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 19;11:916. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00916. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32636746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe Y, Kayakiri H, Satoh S, Inoue T, Sawada Y, Imai K, et al. A novel class of orally active non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonists. 1. Construction of the Basic Framework. J Med Chem. 1998a;41:564–578. - PubMed
-
- Abe Y, Kayakiri H, Satoh S, Inoue T, Sawada Y, Inamura N, et al. A novel class of orally active non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonists. 3. Discovering bioisosteres of the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine moiety. J Med Chem. 1998b;41:4062–4079. - PubMed
-
- Aramori I, Zenkoh J, Morikawa N, Asano M, Hatori C, Sawai H, et al. Nonpeptide mimic of bradykinin with long-acting properties at the bradykinin B2 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;52:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Bachvarov DR, Houle S, Bachvarova M, Bouthillier J, Adam A, Marceau F. Bradykinin B2 receptor endocytosis, recycling, and down-regulation assessed using green fluorescent protein conjugates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:19–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

