Intracoronary versus intravenous abciximab in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: rationale and design of the CICERO trial in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention with thrombus aspiration
- PMID: 19785725
- PMCID: PMC2765937
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-10-90
Intracoronary versus intravenous abciximab in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: rationale and design of the CICERO trial in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention with thrombus aspiration
Abstract
Background: Administration of abciximab during primary percutaneous coronary intervention is an effective adjunctive therapy in the treatment of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Recent small-scaled studies have suggested that intracoronary administration of abciximab during primary percutaneous coronary intervention is superior to conventional intravenous administration. This study has been designed to investigate whether intracoronary bolus administration of abciximab is more effective than intravenous bolus administration in improving myocardial perfusion in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention with thrombus aspiration.
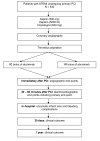
Methods/design: The Comparison of IntraCoronary versus intravenous abciximab administration during Emergency Reperfusion Of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (CICERO) trial is a single-center, prospective, randomized open-label trial with blinded evaluation of endpoints. A total of 530 patients with STEMI undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention are randomly assigned to either an intracoronary or intravenous bolus of weight-adjusted abciximab. The primary end point is the incidence of >70% ST-segment elevation resolution. Secondary end points consist of post-procedural residual ST-segment deviation, myocardial blush grade, distal embolization, enzymatic infarct size, in-hospital bleeding, and clinical outcome at 30 days and 1 year.
Discussion: The CICERO trial is the first clinical trial to date to verify the effect of intracoronary versus intravenous administration of abciximab on myocardial perfusion in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention with thrombus aspiration.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00927615.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intracoronary versus intravenous administration of abciximab in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention with thrombus aspiration: the comparison of intracoronary versus intravenous abciximab administration during emergency reperfusion of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (CICERO) trial.Circulation. 2010 Dec 21;122(25):2709-17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.002741. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 21098442 Clinical Trial.
-
Intracoronary versus intravenous bolus abciximab during primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a randomised trial.Lancet. 2012 Mar 10;379(9819):923-931. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61872-2. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22357109 Clinical Trial.
-
Intracoronary compared with intravenous bolus abciximab application in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: the randomized Leipzig immediate percutaneous coronary intervention abciximab IV versus IC in ST-elevation myocardial infarction trial.Circulation. 2008 Jul 1;118(1):49-57. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.747642. Epub 2008 Jun 16. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18559698 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials comparing intracoronary versus intravenous abciximab in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Am J Cardiol. 2012 Mar 1;109(5):624-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.10.016. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Am J Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22152971 Review.
-
Benefits from intracoronary as compared to intravenous abciximab administration for STEMI patients undergoing primary angioplasty: a meta-analysis of 8 randomized trials.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Jun;222(2):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.02.041. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22483166 Review.
Cited by
-
Bleeding avoidance strategies. Consensus and controversy.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Jun 28;58(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.039. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21700085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeWood MA, Spores J, Notske R, Mouser LT, Burroughs R, Golden MS, Lang HT. Prevalence of total coronary occlusion during the early hours of transmural myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1980;303:897–902. - PubMed
-
- Zijlstra F, Hoorntje JC, de Boer MJ, Reiffers S, Miedema K, Ottervanger JP, van 't Hof AW, Suryapranata H. Long-term benefit of primary angioplasty as compared with thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1413–1419. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199911043411901. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical