The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli effector Cif induces delayed apoptosis in epithelial cells
- PMID: 19786559
- PMCID: PMC2786488
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00860-09
The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli effector Cif induces delayed apoptosis in epithelial cells
Abstract
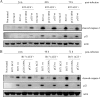
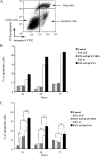
The cycle inhibiting factor (Cif) belongs to a family of bacterial toxins, the cyclomodulins, which modulate the host cell cycle. Upon injection into the host cell by the type III secretion system of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC), Cif induces both G(2) and G(1) cell cycle arrests. The cell cycle arrests correlate with the accumulation of p21(waf1) and p27(kip1) proteins that inhibit CDK-cyclin complexes, whose activation is required for G(1)/S and G(2)/M transitions. Increases of p21 and p27 levels are independent of p53 transcriptional induction and result from protein stabilization through inhibition of the ubiquitin/proteasome degradation pathway. In this study, we show that Cif not only induces cell cycle arrest but also eventually provokes a delayed cell death. Indeed, 48 h after infection with EPEC expressing Cif, cultured IEC-6 intestinal cells were positive for extracellular binding of annexin V and exhibited high levels of cleaved caspase-3 and lactate dehydrogenase release, indicating evidence of apoptosis. Cif was necessary and sufficient for inducing this late apoptosis, and the cysteine residue of the catalytic site was required for Cif activity. These results highlight a more complex role of Cif than previously thought, as a cyclomodulin but also as an apoptosis inducer.
Figures
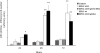

Similar articles
-
EspC, an Autotransporter Protein Secreted by Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Causes Apoptosis and Necrosis through Caspase and Calpain Activation, Including Direct Procaspase-3 Cleavage.mBio. 2016 Jun 21;7(3):e00479-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00479-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27329750 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli cyclomodulin Cif induces G2 arrest of the host cell cycle without activation of the DNA-damage checkpoint-signalling pathway.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Dec;8(12):1910-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00757.x. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16848790
-
Bacterial cyclomodulin Cif blocks the host cell cycle by stabilizing the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Dec;10(12):2496-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01224.x. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18705694
-
Cif type III effector protein: a smart hijacker of the host cell cycle.Future Microbiol. 2009 Sep;4(7):867-77. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.60. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19722840 Review.
-
Cycle inhibiting factors (cifs): cyclomodulins that usurp the ubiquitin-dependent degradation pathway of host cells.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Apr;3(4):356-68. doi: 10.3390/toxins3040356. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069713 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EspC, an Autotransporter Protein Secreted by Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Causes Apoptosis and Necrosis through Caspase and Calpain Activation, Including Direct Procaspase-3 Cleavage.mBio. 2016 Jun 21;7(3):e00479-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00479-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27329750 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial oncogenesis in the colon.Future Microbiol. 2013 Apr;8(4):445-60. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.17. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23534358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 28;23(9):4907. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094907. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563295 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of antibodies to the cytosol: debunking the myths.MAbs. 2014 Jul-Aug;6(4):943-56. doi: 10.4161/mabs.29268. Epub 2014 May 21. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24848507 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic Arrest-Deficient 2 Like 2 (MAD2L2) Interacts with Escherichia coli Effector Protein EspF.Life (Basel). 2021 Sep 15;11(9):971. doi: 10.3390/life11090971. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crane, J. K., B. P. McNamara, and M. S. Donnenberg. 2001. Role of EspF in host cell death induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell. Microbiol. 3:197-211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

