Bacterial toxins induce sustained mRNA expression of the silencing transcription factor klf2 via inactivation of RhoA and Rhophilin 1
- PMID: 19786564
- PMCID: PMC2786462
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00121-09
Bacterial toxins induce sustained mRNA expression of the silencing transcription factor klf2 via inactivation of RhoA and Rhophilin 1
Abstract
Yersiniae bearing the Yersinia virulence plasmid pYV impact the transcriptome of J774A.1 macrophage-like cells in two distinct ways: (i) by suppressing, in a Yersinia outer protein P (YopP)-dependent manner, the induction of inflammatory response genes and (ii) by mRNA induction of the silencing transcription factor klf2. Here we show that klf2 induction by Yersinia enterocolitica occurs in several cell lines of macrophage and squamous and upper gastrointestinal epithelial origin as well as in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Several strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus are equally effective as Y. enterocolitica in inducing klf2 expression. Screening of mutant strains or incubation with recombinant toxins identified the rho-inactivating toxins YopT from Yersinia spp., ExoS from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, EDIN-B from Staphylococcus aureus, and C3bot from Clostridium botulinum as bacterial inducers of klf2 mRNA. klf2 mRNA induction by these toxins does not require de novo protein synthesis. Serum response factor or actin depolymerization does not seem to be involved in regulating klf2 expression in response to bacterial infection. Instead, short hairpin RNA-mediated inactivation of RhoA and its effector rhophilin 1 is sufficient to induce long-term klf2 expression. Thus, bacteria exploit the RhoA-rhophilin signaling cascade to mediate sustained expression of the immunosuppressive transcription factor klf2.
Figures
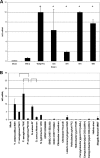
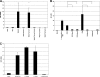
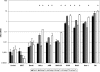
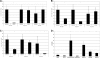
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional responses of murine macrophages to infection with Yersinia enterocolitica.Cell Microbiol. 2004 Apr;6(4):377-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00365.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15009029
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of airway epithelial cells modulates expression of Kruppel-like factors 2 and 6 via RsmA-mediated regulation of type III exoenzymes S and Y.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5893-902. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00489-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988269 Free PMC article.
-
The cytotoxin YopT of Yersinia enterocolitica induces modification and cellular redistribution of the small GTP-binding protein RhoA.J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 8;274(41):29289-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.41.29289. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10506187
-
Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and the host with special reference to virulence plasmid encoded adhesion and humoral immunity.Dan Med Bull. 1992 Apr;39(2):155-72. Dan Med Bull. 1992. PMID: 1611921 Review.
-
The type III cytotoxins of Yersinia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa that modulate the actin cytoskeleton.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;291:147-66. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27511-8_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15984080 Review.
Cited by
-
Yersinia enterocolitica YopT and Clostridium difficile toxin B induce expression of GILZ in epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040730. Epub 2012 Jul 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22792400 Free PMC article.
-
A hemolytic-uremic syndrome-associated strain O113:H21 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli specifically expresses a transcriptional module containing dicA and is related to gene network dysregulation in Caco-2 cells.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 18;12(12):e0189613. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189613. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29253906 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of innate immune responses by Yersinia type III secretion system translocators and effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Oct;15(10):1622-31. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12164. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23834311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of simvastatin on pulmonary effectors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e102200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102200. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010049 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Airway Expression of the Host Bactericidal Enzyme, sPLA2-IIA, by Bacterial Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jul 3;15(7):440. doi: 10.3390/toxins15070440. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37505708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adkins, I., M. Koberle, S. Grobner, E. Bohn, I. B. Autenrieth, and S. Borgmann. 2007. Yersinia outer proteins E, H, P, and T differentially target the cytoskeleton and inhibit phagocytic capacity of dendritic cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 297:235-244. - PubMed
-
- Aepfelbacher, M., C. Trasak, G. Wilharm, A. Wiedemann, K. Trulzsch, K. Krauss, P. Gierschik, and J. Heesemann. 2003. Characterization of YopT effects on Rho GTPases in Yersinia enterocolitica-infected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278:33217-33223. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad, N., and J. B. Lingrel. 2005. Kruppel-like factor 2 transcriptional regulation involves heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins and acetyltransferases. Biochemistry 44:6276-6285. - PubMed
-
- Aktories, K., and J. T. Barbieri. 2005. Bacterial cytotoxins: targeting eukaryotic switches. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:397-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

