Treatment response of cystic echinococcosis to benzimidazoles: a systematic review
- PMID: 19787039
- PMCID: PMC2745697
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000524
Treatment response of cystic echinococcosis to benzimidazoles: a systematic review
Abstract
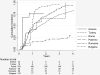
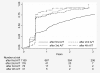
Over the past 30 years, benzimidazoles have increasingly been used to treat cystic echinococcosis (CE). The efficacy of benzimidazoles, however, remains unclear. We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, SIGLE, and CCTR to identify studies on benzimidazole treatment outcome. A large heterogeneity of methods in 23 reports precluded a meta-analysis of published results. Specialist centres were contacted to provide individual patient data. We conducted survival analyses for cyst response defined as inactive (CE4 or CE5 by the ultrasound-based World Health Organisation [WHO] classification scheme) or as disappeared. We collected data from 711 treated patients with 1,308 cysts from six centres (five countries). Analysis was restricted to 1,159 liver and peritoneal cysts. Overall, 1-2 y after initiation of benzimidazole treatment 50%-75% of active C1 cysts were classified as inactive/disappeared compared to 30%-55% of CE2 and CE3 cysts. Further in analyzing the rate of inactivation/disappearance with regard to cyst size, 50%-60% of cysts <6 cm responded to treatment after 1-2 y compared to 25%-50% of cysts >6 cm. However, 25% of cysts reverted to active status within 1.5 to 2 y after having initially responded and multiple relapses were observed; after the second and third treatment 60% of cysts relapsed within 2 y. We estimated that 2 y after treatment initiation 40% of cysts are still active or become active again. The overall efficacy of benzimidazoles has been overstated in the past. There is an urgent need for a pragmatic randomised controlled trial that compares standardized benzimidazole therapy on responsive cyst stages with the other treatment modalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Junghanss T, Da Silva A, Horton J, Chiodini P, Brunetti E. The clinical management of cystic echinococcosis: state of the art, problems, and perspectives. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:301–311. - PubMed
-
- Pawlowski ZS, Eckert J, Vuitton DA, Ammann RW, Kern P, et al. Echinococcosis in humans: clinical aspects, diagnosis and treatment. 2001. pp. 20–47. WHO manual on echinococcosis in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern.
-
- Horton J. Albendazole for the treatment of echinococcosis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2003;17:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Lin DY, Wei LJ. The robust inference for the Cox proportional hazards model. J Am Stat Assoc. 1989;84:1074–84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

