Roles of specific membrane lipid domains in EGF receptor activation and cell adhesion molecule stabilization in a developing olfactory system
- PMID: 19787046
- PMCID: PMC2746287
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007222
Roles of specific membrane lipid domains in EGF receptor activation and cell adhesion molecule stabilization in a developing olfactory system
Abstract
Background: Reciprocal interactions between glial cells and olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) cause ORN axons entering the brain to sort, to fasciculate into bundles destined for specific glomeruli, and to form stable protoglomeruli in the developing olfactory system of an experimentally advantageous animal species, the moth Manduca sexta. Epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs) and the cell adhesion molecules (IgCAMs) neuroglian and fasciclin II are known to be important players in these processes.
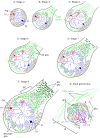
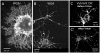
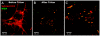
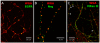
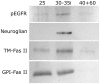
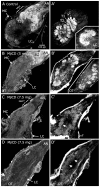
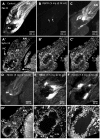
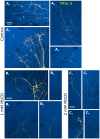
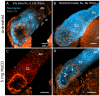
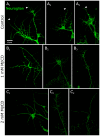
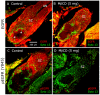
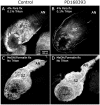
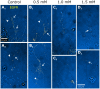
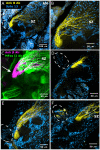
Methodology/principal findings: We report in situ and cell-culture studies that suggest a role for glycosphingolipid-rich membrane subdomains in neuron-glia interactions. Disruption of these subdomains by the use of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin results in loss of EGFR activation, depletion of fasciclin II in ORN axons, and loss of neuroglian stabilization in the membrane. At the cellular level, disruption leads to aberrant ORN axon trajectories, small antennal lobes, abnormal arrays of olfactory glomerul, and loss of normal glial cell migration.
Conclusions/significance: We propose that glycosphingolipid-rich membrane subdomains (possible membrane rafts or platforms) are essential for IgCAM-mediated EGFR activation and for anchoring of neuroglian to the cytoskeleton, both required for normal extension and sorting of ORN axons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gibson NJ, Rossler W, Nighorn AJ, Oland LA, Hildebrand JG, et al. Neuron-glia communication via nitric oxide is essential in establishing antennal-lobe structure in Manduca sexta. Dev Biol. 2001;240:326–339. - PubMed
-
- Oland LA, Tolbert LP. Key interactions between neurons and glial cells during neural development in insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 2003;48:89–110. - PubMed
-
- Tolbert LP, Oland LA, Tucker ES, Gibson NJ, Higgins MR, et al. Bidirectional influences between neurons and glial cells in the developing olfactory system. Prog Neurobiol. 2004;73:73–105. - PubMed
-
- Treloar HB, Purcell AL, Greer CA. Glomerular formation in the developing rat olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 1999;413:289–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

