TNF receptors differentially signal and are differentially expressed and regulated in the human heart
- PMID: 19788501
- PMCID: PMC3517885
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02831.x
TNF receptors differentially signal and are differentially expressed and regulated in the human heart
Abstract
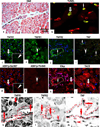
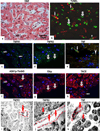
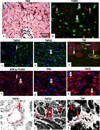
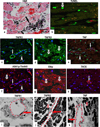
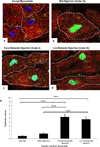
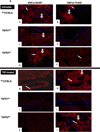
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) utilizes two receptors, TNFR1 and 2, to initiate target cell responses. We assessed expression of TNF, TNFRs and downstream kinases in cardiac allografts, and compared TNF responses in heart organ cultures from wild-type ((WT)C57BL/6), TNFR1-knockout ((KO)), TNFR2(KO), TNFR1/2(KO) mice. In nonrejecting human heart TNFR1 was strongly expressed coincidentally with inactive apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1) in cardiomyocytes (CM) and vascular endothelial cells (VEC). TNFR2 was expressed only in VEC. Low levels of TNF localized to microvessels. Rejecting cardiac allografts showed increased TNF in microvessels, diminished TNFR1, activation of ASK1, upregulated TNFR2 co-expressed with activated endothelial/epithelial tyrosine kinase (Etk), increased apoptosis and cell cycle entry in CM. Neither TNFR was expressed significantly by cardiac fibroblasts. In (WT)C57BL/6 myocardium, TNF activated both ASK1 and Etk, and increased both apoptosis and cell cycle entry. TNF-treated TNFR1(KO) myocardium showed little ASK1 activation and apoptosis but increased Etk activation and cell cycle entry, while TNFR2(KO) myocardium showed little Etk activation and cell cycle entry but increased ASK1 activation and apoptosis. These observations demonstrate independent regulation and differential functions of TNFRs in myocardium, consistent with TNFR1-mediated cell death and TNFR2-mediated repair.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interests
Figures




Similar articles
-
TNFR1- and TNFR2-mediated signaling pathways in human kidney are cell type-specific and differentially contribute to renal injury.FASEB J. 2005 Oct;19(12):1637-45. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3841com. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 16195372
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor expression and signaling in renal cell carcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2010 Aug;177(2):943-54. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091218. Epub 2010 Jun 21. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20566746 Free PMC article.
-
Differential functions of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 signaling in ischemia-mediated arteriogenesis and angiogenesis.Am J Pathol. 2006 Nov;169(5):1886-98. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060603. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17071609 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
-
Transmembrane TNF and Its Receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2 in Mycobacterial Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 22;22(11):5461. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115461. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Etanercept Ameliorates Cardiac Fibrosis in Rats with Diet-Induced Obesity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 1;14(4):320. doi: 10.3390/ph14040320. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916242 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of intra-alveolar p55 TNF receptor attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury.Thorax. 2012 Mar;67(3):244-51. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200590. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Thorax. 2012. PMID: 22156959 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of Lin28-TNFR2 signalling in cardiac stem cell activation and differentiation.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Apr;23(4):0. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14202. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30734494 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of TNF receptor subtype expression and signaling on pulmonary endothelial cells in mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):L781-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00326.2010. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21378027 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned medium from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates cardiac injury induced by Movento in male rats: role of oxidative stress and inflammation.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 22;26(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00847-w. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39844289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB. Antitumor necrosis factor therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a review of agents, pharmacology, clinical results, and safety. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1999;5(2):119–133. - PubMed
-
- Nikolaus S, Schreiber S. Anti-TNF biologics in the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Internist (Berl) 2008;49(8):947–943. - PubMed
-
- Meldrum DR. Tumor necrosis factor in the heart. Am J Physiol. 1998;274(3 Pt 2):R577–R595. - PubMed
-
- Muller-Ehmsen J, Schwinger RH. TNF and congestive heart failure: therapeutic possibilities. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2004;8(3):203–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

