UVR exposure sensitizes keratinocytes to DNA adduct formation
- PMID: 19789301
- PMCID: PMC2758323
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0125
UVR exposure sensitizes keratinocytes to DNA adduct formation
Abstract
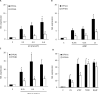
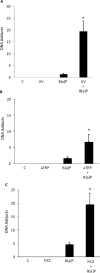
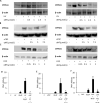
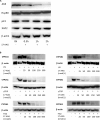
UV radiation (UVR) and exposure to tobacco smoke, a source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), have been linked to skin carcinogenesis. UVR-mediated activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) stimulates the transcription of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, which encode proteins that convert PAH to genotoxic metabolites. We determined whether UVR exposure sensitized human keratinocytes to PAH-induced DNA adduct formation. UVR exposure induced CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in HaCaT cells, an effect that was mimicked by photooxidized tryptophan (aTRP) and FICZ, a component of aTRP. UVR exposure or pretreatment with aTRP or FICZ also sensitized cells to benzo(a)pyrene (B[a]P)-induced DNA adduct formation. alphaNF, an AhR antagonist, suppressed UVR-, aTRP-, and FICZ-mediated induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 and inhibited B[a]P-induced DNA adduct formation. Treatment with 17-AAG, an Hsp90 inhibitor, caused a marked decrease in levels of AhR; inhibited UVR-, aTRP-, and FICZ-mediated induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1; and blocked the sensitization of HaCaT cells to B[a]P-induced DNA adduct formation. FICZ has been suggested to be a physiologic ligand of the AhR that may have systemic effects. Hence, studies of FICZ were also carried out in MSK-Leuk1 cells, a model of oral leukoplakia. Pretreatment with alpha-naphthoflavone or 17-AAG blocked FICZ-mediated induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, and suppressed the increased B[a]P-induced DNA adduct formation. Collectively, these results suggest that sunlight may activate AhR signaling and thereby sensitize cells to PAH-mediated DNA adduct formation. Antagonists of AhR signaling may have a role in the chemoprevention of photocarcinogenesis.
Figures
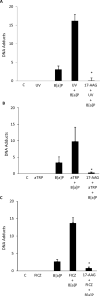
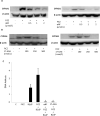
References
-
- Aubry F, MacGibbon B. Risk factors of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. A case-control study in the Montreal region. Cancer. 1985;55:907–911. - PubMed
-
- Grodstein F, Speizer FE, Hunter DJ. A prospective study of incident squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in the nurses' health study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87:1061–1066. - PubMed
-
- De Hertog SA, Wensveen CA, Bastiaens MT, et al. Relation between smoking and skin cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Kanjilal S, Strom SS, Clayman GL, et al. p53 mutations in nonmelanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: molecular evidence for field cancerization. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3604–3609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

