A novel reduced immunogenicity bispecific targeted toxin simultaneously recognizing human epidermal growth factor and interleukin-4 receptors in a mouse model of metastatic breast carcinoma
- PMID: 19789305
- PMCID: PMC2756320
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0696
A novel reduced immunogenicity bispecific targeted toxin simultaneously recognizing human epidermal growth factor and interleukin-4 receptors in a mouse model of metastatic breast carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a targeted biological drug that when systemically injected can penetrate to metastatic breast cancer tumors, one needs a drug of high potency and reduced immunogenicity. Thus, we bioengineered a novel bispecific ligand-directed toxin (BLT) targeted by dual high-affinity cytokines with a PE(38)KDEL COOH terminus. Our purpose was to reduce toxin immunogenicity using mutagenesis, measure the ability of mutated drug to elicit B-cell antitoxin antibody responses, and show that mutated drug was effective against systemic breast cancer in vivo.
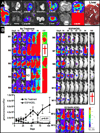
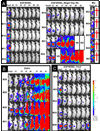
Experimental design: A new BLT was created in which both human epidermal growth factor (EGF) and interleukin 4 cytokines were cloned onto the same single-chain molecule with truncated Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE(38)). Site-specific mutagenesis was used to mutate amino acids in seven key epitopic toxin regions that dictate B-cell generation of neutralizing antitoxin antibodies. Bioassays were used to determine whether mutation reduced potency, and ELISA studies were done to determine whether antitoxin antibodies were reduced. Finally, a genetically altered luciferase xenograft model was used; this model could be imaged in real time to determine the effect on the systemic malignant human breast cancer MDA-MB-231.
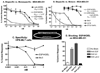
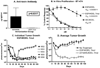
Results: EGF4KDEL 7mut was significantly effective against established systemic human breast cancer and prevented metastatic spread. Mutagenesis reduced immunogenicity by approximately 90% with no apparent loss in in vitro or in vivo activity.
Conclusions: Because EGF4KDEL 7mut was highly effective even when we waited 26 days to begin therapy and because immunogenicity was significantly reduced, we can now give multiple drug treatments for chemotherapy-refractory breast cancer in clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kreitman RJ, Squires DR, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 (BL22) in patients with B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6719–6729. - PubMed
-
- Kioi M, Shimamura T, Nakashima H, Hirota M, Tohnai I, Husain SR, Puri RK. IL-13 cytotoxin has potent antitumor activity and synergizes with paclitaxel in a mouse model of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:1440–1448. - PubMed
-
- Hassan R, Bullock S, Premkumar A, et al. Phase I study of SS1P, a recombinant antimesothelin immunotoxin given as a bolus I.V. infusion to patients with mesothelinexpressing mesothelioma, ovarian and pancreatic cancers. Clin.Cancer Res. 2007;13:5144–5149. - PubMed
-
- Onda M, Nagata S, FitzGerald DJ, et al. Characterization of the B cell epitopes associated with a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE38) used to make immunotoxins for the treatment of cancer patients. J Immunol. 2006;177:8822–8834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

