CCR5 is involved in resolution of inflammation in proteoglycan-induced arthritis
- PMID: 19790057
- PMCID: PMC2826270
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24842
CCR5 is involved in resolution of inflammation in proteoglycan-induced arthritis
Abstract
Objective: CCR5 and its ligands (CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5) may play a role in inflammatory cell recruitment into the joint. However, it was recently reported that CCR5 on T cells and neutrophils acts as a decoy receptor for CCL3 and CCL5 to assist in the resolution of inflammation. The aim of this study was to determine whether CCR5 functions as a proinflammatory or antiinflammatory mediator in arthritis, by examining the role of CCR5 in proteoglycan (PG)-induced arthritis (PGIA).
Methods: Arthritis was induced by immunizing wild-type (WT) and CCR5-deficient (CCR5(-/-)) BALB/c mice with human PG in adjuvant. The onset and severity of PGIA were monitored over time. Met-RANTES was used to block CCR5 in vivo. Arthritis was transferred to SCID mice, using spleen cells from arthritic WT and CCR5(-/-) mice. The expression of cytokines and chemokines was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
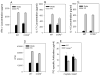
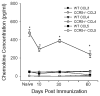
Results: In CCR5(-/-) mice and WT mice treated with the CCR5 inhibitor Met-RANTES, exacerbated arthritis developed late in the disease course. The increase in arthritis severity in CCR5(-/-) mice correlated with elevated serum levels of CCL5. However, exacerbated arthritis was not intrinsic to the CCR5(-/-) lymphoid cells, because the arthritis that developed in SCID mouse recipients was similar to that in WT and CCR5(-/-) mice. CCR5 expression in the SCID mouse was sufficient to clear CCL5, because serum levels of CCL5 were the same in SCID mouse recipients receiving cells from either WT or CCR5(-/-) mice.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that CCR5 is a key player in controlling the resolution of inflammation in experimental arthritis.
Figures



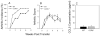
Similar articles
-
CCL2/CCR2, but not CCL5/CCR5, mediates monocyte recruitment, inflammation and cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 May;76(5):914-922. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210426. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27965260 Free PMC article.
-
Development of inflammation in proteoglycan-induced arthritis is dependent on Fc gamma R regulation of the cytokine/chemokine environment.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5851-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5851. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421967
-
Development of proteoglycan-induced arthritis depends on T cell-supported autoantibody production, but does not involve significant influx of T cells into the joints.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):R44. doi: 10.1186/ar2954. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20298547 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Polymorphism at CCL5 Is Associated With Protection in Chagas' Heart Disease: Antagonistic Participation of CCR1+ and CCR5+ Cells in Chronic Chagasic Cardiomyopathy.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 11;9:615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00615. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29696014 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine receptor CCR5 deficiency exacerbates cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):G1089-99. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00571.2005. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16891300
Cited by
-
Unicompartmental and bicompartmental knee osteoarthritis show different patterns of mononuclear cell infiltration and cytokine release in the affected joints.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Apr;180(1):143-54. doi: 10.1111/cei.12486. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25393692 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preventive CCL2/CCR2 Axis Blockade Suppresses Osteoclast Activity in a Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Reducing Homing of CCR2hi Osteoclast Progenitors to the Affected Bone.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 3;12:767231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.767231. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925336 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia Responses to Pro-inflammatory Stimuli (LPS, IFNγ+TNFα) and Reprogramming by Resolving Cytokines (IL-4, IL-10).Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Jul 24;12:215. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00215. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30087595 Free PMC article.
-
The dual-function chemokine receptor CCR2 drives migration and chemokine scavenging through distinct mechanisms.Sci Signal. 2023 Jan 31;16(770):eabo4314. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abo4314. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 36719944 Free PMC article.
-
CCR5 Is Involved in Interruption of Pregnancy in Mice Infected with Toxoplasma gondii during Early Pregnancy.Infect Immun. 2017 Aug 18;85(9):e00257-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00257-17. Print 2017 Sep. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28630065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2005;204:55–73. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(6):429–42. - PubMed
-
- Koch AE. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: future targets? Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(3):710–21. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A, Mackay CR. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in T-cell priming and Th1/Th2-mediated responses. Immunol Today. 1998;19(12):568–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

