Trimethylamine N-oxide influence on the backbone of proteins: an oligoglycine model
- PMID: 19790265
- PMCID: PMC2805780
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.22598
Trimethylamine N-oxide influence on the backbone of proteins: an oligoglycine model
Abstract
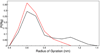
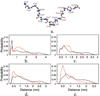
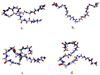
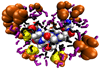
The study of organic osmolytes has been pivotal in demonstrating the role of solvent effects on the protein backbone in the folding process. Although a thermodynamic description of the interactions between the protein backbone and osmolyte has been well defined, the structural analysis of the effect of osmolyte on the protein backbone has been incomplete. Therefore, we have performed simulations of a peptide backbone model, glycine(15), in protecting osmolyte trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) solution, in order to determine the effect of the solution structure on the conformation of the peptide backbone. We show that the models chosen show that the ensemble of backbone structures shifts toward a more collapsed state in TMAO solution as compared with pure water solution. The collapse is consistent with preferential exclusion of the osmolyte caused by unfavorable interactions between osmolyte and peptide backbone. The exclusion is caused by strong triplet correlations of osmolyte, water, and peptide backbone. This provides a clear mechanism showing that even a modest concentration of TMAO forces the protein backbone to adopt a more collapsed structure in the absence of side chain effects.
Figures

References
-
- Hochachka PW, Somero GN. Biochemical Adaptation. Mechanism and process in physiological evolution. New York: Oxford University Press; 2002.
-
- Timasheff SN. Control of protein stability and reactions by weakly interacting cosolvents: the simplicity of the complicated. Adv Protein Chem. 1998;51:355–432. - PubMed
-
- Nozaki Y, Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and related compounds in aqueous urea solutions. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1963;238:4074–4081. - PubMed
-
- Tanford C. Isothermal unfolding of globular proteins in aqueous urea solutions. Journal of American Chemical Society. 1964;86:2050–2059.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

