Multipoint linkage analysis and heterogeneity testing in 20 X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families
- PMID: 1979051
- PMCID: PMC6174538
- DOI: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90284-2
Multipoint linkage analysis and heterogeneity testing in 20 X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families
Abstract
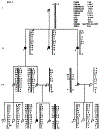
Using multipoint linkage analysis in 20 families segregating for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP), the lod scores on a map of eight RFLP loci were obtained. Our results indicate that under the hypothesis of homogeneity the maximal multipoint lod score supports one disease locus located slightly distal to OTC at Xp21.1. Heterogeneity testing for two XLRP loci suggested that a second XLRP locus may be located 8.5 cM proximal to DXS28 at Xp21.3. Further heterogeneity testing for three disease loci failed to detect a third XLRP locus proximal to DXS7 in any of our 20 XLRP families.
Figures












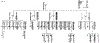
References
-
- Bhattacharya SS, Wright AF, Clayton JF, Price WH, Phillips CI, Mckeown CME, Jay M, Bird AC, Pearson PL, Southern EM, AND Evans HJ (1984). Close genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and a recombinant DNA probe L1.28. Nature (London) 309:253–255. - PubMed
-
- Denton MJ, Chen JD, Serravalle S, Colley P, Halliday FB, AND Donald J (1988). Analysis of linkage relationships of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa with the following Xp loci: L1.28, OTC, XJ1.1, pERT87, and C7. Hum. Genet 78:60–64. - PubMed
-
- de Saint-Basile G, Bohlek MC, Fischer A, Cartron J, Dufier JL, Griselli C, AND Orkin SH (1988). X p21 D N A microdeletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and the McLeod phenotype. Hum. Genet 80: 85–89. - PubMed
-
- Drayna D, AND White R (1985). The genetic linkage map of the X chromosome. Science 230: 753–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

