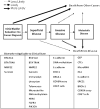
Clinical states model for biomarkers in bladder cancer
- PMID: 19792967
- PMCID: PMC3705955
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.09.57
Clinical states model for biomarkers in bladder cancer
Abstract
Bladder cancer is a significant healthcare problem in the USA, with a high recurrence rate, the need for expensive continuous surveillance and limited treatment options for patients with advanced disease. Research has contributed to an understanding of the molecular pathways involved in the development and progression of bladder cancer, and that understanding has led to the discovery of potentially diagnostic, predictive and prognostic biomarkers. In this review, a clinical states model of bladder cancer is introduced and integrated into a paradigm for biomarker development. Biomarkers are systematically incorporated with predefined end points to aid in clinical management.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An online tool for evaluating diagnostic and prognostic gene expression biomarkers in bladder cancer.BMC Urol. 2015 Jul 1;15:59. doi: 10.1186/s12894-015-0056-z. BMC Urol. 2015. PMID: 26126604 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder cancer biomarkers: review and update.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(6):2395-403. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.6.2395. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24761840 Review.
-
Molecular markers in bladder cancer.World J Urol. 2019 Jan;37(1):31-40. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2503-4. Epub 2018 Sep 26. World J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30259123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemistry Biomarkers in Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017 Mar;25(3):178-183. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000280. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 26574637
-
Considerations on the use of diagnostic markers in management of patients with bladder cancer.World J Urol. 2008 Feb;26(1):39-44. doi: 10.1007/s00345-007-0232-1. Epub 2007 Dec 19. World J Urol. 2008. PMID: 18092171 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted roles of mucins family in lung cancer: from prognostic biomarkers to promising targets.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1608140. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1608140. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40655139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular expression profiling with respect to KEGG hsa05219 pathway.Ecancermedicalscience. 2011;5:189. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2011.189. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Ecancermedicalscience. 2011. PMID: 22276047 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from animal models of bladder cancer: recent advances, challenges, and opportunities.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(34):57766-57781. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17714. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological basis in the pathogenesis and treatment of bladder cancer.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015 Feb;11(2):265-79. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.983082. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25391391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A quantitative proteomic analysis uncovers the relevance of CUL3 in bladder cancer aggressiveness.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053328. Epub 2013 Jan 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whelan P. Bladder Cancer--Contemporary Dilemmas in Its Management. European Urology. 2008;53(1):24–26. - PubMed
-
- Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Redaelli A, Laskin B, Hauser R. The health economics of bladder cancer: a comprehensive review of the published literature. PharmacoEconomics. 2003;21(18):1315–1330. - PubMed
-
- Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(3):666–675. - PubMed
-
- von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, et al. Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(21):4602–4608. - PubMed
-
- Bishop J, Weinberg RA. Molecular Oncology. Scientific American, Inc; New York: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical