High expression of the evolutionarily conserved alpha/beta hydrolase domain containing 6 (ABHD6) in Ewing tumors
- PMID: 19793082
- PMCID: PMC11158961
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01347.x
High expression of the evolutionarily conserved alpha/beta hydrolase domain containing 6 (ABHD6) in Ewing tumors
Abstract
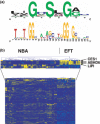
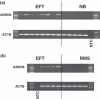
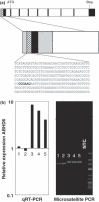
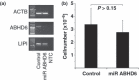
Despite improvements in the treatment of patients with Ewing family tumors (EFT), the prognosis for patients with advanced disease is still unsatisfactory. Recently, we identified lipase I as an EFT-associated gene that might be interesting for the development of new immunological or pharmacological treatment strategies. Lipase I is a member of the large protein superfamilies of alpha/beta hydrolases and serine hydrolases. In the present paper we describe high expression of another member of these superfamilies in EFT. By DNA microarray data base mining we found exceptional high expression of alpha/beta hydrolase domain containing 6 (ABHD6) in EFT but not in other sarcomas. Expression of ABHD6 in EFT correlated with expression of another EFT-associated gene, aristaless. Analysis of ABHD6-associated GGAA microsatellites revealed shorter microsatellites in EFT with lack of ABHD6 expression. ABHD6 homologues were found in varying chordata but not in other animal species. Based on homology modeling we predicted the 3D-structure of ABHD6, which shows high similarity with bacterial homoserine transacetylases. High expression of ABHD6 in EFT in comparison to normal tissues and other tumors suggests that ABHD6 might be an interesting new diagnostic or therapeutic target for EFT. However, knock down of ABHD6 in EFT cells did not inhibit tumor cell growth.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of multiple membrane-associated phospholipase A1 beta transcript variants and lysophosphatidic acid receptors in Ewing tumor cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Oct;38(7):4619-28. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0595-z. Epub 2010 Dec 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21132378
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting α/β-Hydrolase domain-containing 6 (ABHD6).Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jul 15;198:112353. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112353. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32371333 Review.
-
Comparative molecular field analysis and molecular dynamics studies of α/β hydrolase domain containing 6 (ABHD6) inhibitors.J Mol Model. 2015 Oct;21(10):250. doi: 10.1007/s00894-015-2789-8. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Mol Model. 2015. PMID: 26350245 Free PMC article.
-
Monoacylglycerol signalling and ABHD6 in health and disease.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Sep;19 Suppl 1:76-89. doi: 10.1111/dom.13008. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28880480 Review.
-
Characterization of Ewing sarcoma associated cancer/testis antigens.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Mar;14(3):254-61. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23298. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23291981 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of human α/β-hydrolase domain containing 6 (ABHD6) and 12 (ABHD12).J Lipid Res. 2012 Nov;53(11):2413-24. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M030411. Epub 2012 Sep 11. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22969151 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa esterase PA2949, a bacterial homolog of the human membrane esterase ABHD6: expression, purification and crystallization.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019 Apr 1;75(Pt 4):270-277. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X19002152. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019. PMID: 30950828 Free PMC article.
-
α/β-Hydrolase Domain (ABHD) Inhibitors as New Potential Therapeutic Options against Lipid-Related Diseases.J Med Chem. 2021 Jul 22;64(14):9759-9785. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00624. Epub 2021 Jul 2. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34213320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescence-Based Enzyme Activity Assay: Ascertaining the Activity and Inhibition of Endocannabinoid Hydrolytic Enzymes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 13;25(14):7693. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147693. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha/Beta-Hydrolase Domain-Containing 6: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 2;12:784202. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.784202. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34925039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Janknecht R. EWS‐ETS oncoproteins: the linchpins of Ewing tumors. Gene 2005; 363: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Maksimenko A, Lambert G, Bertrand JR, Fattal E, Couvreur P, Malvy C. Therapeutic potentialities of EWS‐Fli‐1 mRNA‐targeted vectorized antisense oligonucleotides. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 1002: 72–7. - PubMed
-
- Toub N, Bertrand JR, Tamaddon A et al. Efficacy of siRNA nanocapsules targeted against the EWS‐Fli1 oncogene in Ewing sarcoma. Pharm Res 2006; 23: 892–900. - PubMed
-
- Staege MS, Hutter C, Neumann I et al. DNA microarrays reveal relationship of Ewing family tumors to both endothelial and fetal neural crest‐derived cells and define novel targets. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 8213–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

