Incidental appendectomy during endoscopic surgery
- PMID: 19793480
- PMCID: PMC3015983
Incidental appendectomy during endoscopic surgery
Abstract
Background and objectives: The first laparoscopic appendectomy was performed over 25 years ago, and yet controversy still exists over the open method vs. the laparoscopic approach, and whether an incidental appendectomy is warranted. This study aimed to evaluate our experience in performing a laparoscopic incidental appendectomy and to address these issues.
Methods: A total of 772 laparoscopic appendectomies were performed and analyzed and statistically evaluated.
Results: Mean age of the patients was 30.8+/-7.0 years. Mean operating time for an incidental appendectomy was 12.3+/-4.5 minutes. Most common pathology result was adhesions, and the rarest was endometriosis. Of patients with confirmed appendicitis, 75.8% did not have an initial preoperative diagnosis of appendicitis. When warranted, 103 (13.3%) patients underwent a second-look laparoscopy: 75.5% had no adhesions, 23.5% had mild adhesions, 2% had moderate adhesions. Backward elimination logistic regression revealed that endometriosis (P=0.016), endometrioma (P=0.039), pelvic or abdominal adhesions (P=0.015) were associated with a reduced likelihood of encountering appendicitis on pathology examination. The complication rate was 0.13%. Anesthesia cost was lower for an incidental appendectomy compared with an urgent one.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic incidental appendectomy is safe and quick to perform. Due to the complex nature of confirming the diagnosis of pelvic and abdominal pain, this study supports the routine performance of an incidental appendectomy in the female patient.
Figures
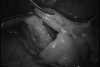
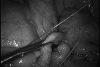

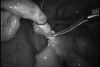

References
-
- Semm K. Endoscopic appendectomy. Endoscopy. 1983;15:59–64 - PubMed
-
- Laine S, Rantala A, Gullichsen R, Ovaska J. Laparoscopic appendectomy-is it worthwhile? A prospective, randomized study in young women Surg Endosc. 1997;11:95–97 - PubMed
-
- Macarulla E, Vallet J, Abad JM, Hussein H, Fernandez E, Nieto B. Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 1997;7(4):335–339 - PubMed
-
- Chung RS, Rowland DY, Li P, Diaz J. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of laparoscopic versus conventional appendectomy. Am J Surg. 1999;177(3):250–256 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
