Construct Validity of the Holistic Complementary and Alternative Medicines Questionnaire (HCAMQ)-An Investigation Using Modern Psychometric Approaches
- PMID: 19793835
- PMCID: PMC3135427
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nep141
Construct Validity of the Holistic Complementary and Alternative Medicines Questionnaire (HCAMQ)-An Investigation Using Modern Psychometric Approaches
Abstract
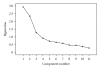
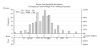
The scientific basis of efficacy studies of complementary medicine requires the availability of validated measures. The Holistic Complementary and Alternative Medicine Questionnaire (HCAMQ) is one such measure. This article aimed to examine its construct validity, using a modern psychometric approach. The HCAMQ was completed by 221 patients (mean age 66.8, SD 8.29, 58% females) with chronic stable pain predominantly from a single joint (hip or knee) of mechanical origin, waiting for a hip (40%) or knee (60%) joint replacement, on enrolment in a study investigating the effects of acupuncture and placebo controls. The HCAMQ contains a Holistic Health (HH) Subscale (five items) and a CAM subscale (six items). Validity of the subscales was tested using Cronbach alpha's, factor analysis, Mokken scaling and Rasch analysis, which did not support the original two-factor structure of the scale. A five-item HH subscale and a four-item CAM subscale (worded in a negative direction) fitted the Rasch model and were unidimensional (χ2 = 8.44, P = 0.39, PSI = 0.69 versus χ2 = 17.33, P = 0.03, PSI = 0.77). Two CAM items (worded in the positive direction) had significant misfit. In conclusion, we have shown that the original two-factor structure of the HCAMQ could not be supported but that two valid shortened subscales can be used, one for HH Beliefs (four-item HH), and the other for CAM Beliefs (four-item CAM). It is recommended that consideration is given to rewording the two discarded positively worded CAM questions to enhance construct validity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developing a measure of attitudes: the holistic complementary and alternative medicine questionnaire.Complement Ther Med. 2003 Mar;11(1):33-8. doi: 10.1016/s0965-2299(02)00113-9. Complement Ther Med. 2003. PMID: 12667973
-
Rasch analysis resulted in an improved Norwegian version of the Pain Attitudes and Beliefs Scale (PABS).Scand J Pain. 2016 Oct;13:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.sjpain.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Scand J Pain. 2016. PMID: 28850539
-
Development and validation of a 6-item Revised UCLA Loneliness Scale (RULS-6) using Rasch analysis.Br J Health Psychol. 2020 May;25(2):233-256. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12404. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Br J Health Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31999891
-
The consultation and relational empathy measure: an investigation of its scaling structure.Disabil Rehabil. 2012;34(6):503-9. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2011.610493. Epub 2011 Oct 8. Disabil Rehabil. 2012. PMID: 21981037
-
Construct validity of a 12-item WOMAC for assessment of femoro-acetabular impingement and osteoarthritis of the hip.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008 Sep;16(9):1032-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2008.02.006. Epub 2008 Jul 3. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008. PMID: 18602281
Cited by
-
Symptom clusters associated with complementary and alternative medicine use by cancer patients: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 14;18(12):e0294641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294641. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38096236 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic symptoms and holistic thinking as major dimensions behind modern health worries.Int J Behav Med. 2014;21(5):869-76. doi: 10.1007/s12529-013-9363-5. Int J Behav Med. 2014. PMID: 24136400
-
Yoga and massage are associated with small experimental placebo effects in chronic orofacial pain.Eur J Pain. 2023 Aug;27(7):816-830. doi: 10.1002/ejp.2111. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Eur J Pain. 2023. PMID: 36932918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arthritis Care. OA Nation. London, UK: Arthritis Care; 2004.
-
- Kauppila A-M, Kyllönen E, Mikkonen P, et al. Disability in end-stage knee osteoarthritis. Disability and Rehabilitation. 2009;31(5):370–380. - PubMed
-
- Ernst E. Evaluation of complementary/alternative medicine. Zeitschrift für Arztliche Fortbildung und Qualitatssicherung. 2007;101(5):313–315. - PubMed
-
- Ernst E. Complementary treatments in rheumatic diseases. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 2008;34(2):455–467. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources