Neural representation of hand kinematics during prehension in posterior parietal cortex of the macaque monkey
- PMID: 19793876
- PMCID: PMC2804418
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.90942.2008
Neural representation of hand kinematics during prehension in posterior parietal cortex of the macaque monkey
Abstract
Studies of hand manipulation neurons in posterior parietal cortex of monkeys suggest that their spike trains represent objects by the hand postures needed for grasping or by the underlying patterns of muscle activation. To analyze the role of hand kinematics and object properties in a trained prehension task, we correlated the firing rates of neurons in anterior area 5 with hand behaviors as monkeys grasped and lifted knobs of different shapes and locations in the workspace. Trials were divided into four classes depending on the approach trajectory: forward, lateral, and local approaches, and regrasps. The task factors controlled by the animal-how and when he used the hand-appeared to play the principal roles in modulating firing rates of area 5 neurons. In all, 77% of neurons studied (58/75) showed significant effects of approach style on firing rates; 80% of the population responded at higher rates and for longer durations on forward or lateral approaches that included reaching, wrist rotation, and hand preshaping prior to contact, but only 13% distinguished the direction of reach. The higher firing rates in reach trials reflected not only the arm movements needed to direct the hand to the target before contact, but persisted through the contact, grasp, and lift stages. Moreover, the approach style exerted a stronger effect on firing rates than object features, such as shape and location, which were distinguished by half of the population. Forty-three percent of the neurons signaled both the object properties and the hand actions used to acquire them. However, the spread in firing rates evoked by each knob on reach and no-reach trials was greater than distinctions between different objects grasped with the same approach style. Our data provide clear evidence for synergies between reaching and grasping that may facilitate smooth, coordinated actions of the arm and hand.
Figures

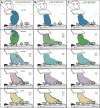





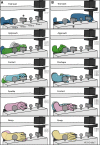


Similar articles
-
Neurophysiology of prehension. I. Posterior parietal cortex and object-oriented hand behaviors.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jan;97(1):387-406. doi: 10.1152/jn.00558.2006. Epub 2006 Sep 13. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 16971679 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiology of prehension. III. Representation of object features in posterior parietal cortex of the macaque monkey.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Dec;98(6):3708-30. doi: 10.1152/jn.00609.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 17. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17942625 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of neuronal firing rates in somatosensory and posterior parietal cortex during prehension.Exp Brain Res. 2001 Apr;137(3-4):269-91. doi: 10.1007/s002210000660. Exp Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11355375
-
Vision for Prehension in the Medial Parietal Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Feb 1;27(2):1149-1163. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv302. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 26656999 Review.
-
The posterior parietal area V6A: An attentionally-modulated visuomotor region involved in the control of reach-to-grasp action.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Oct;141:104823. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104823. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35961383 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural population dynamics in motor cortex are different for reach and grasp.Elife. 2020 Nov 17;9:e58848. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58848. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33200745 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary contribution of the medial and lateral human parietal cortex to grasping: a repetitive TMS study.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Apr 25;33(9):5122-5134. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac404. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36245221 Free PMC article.
-
Neural representation during visually guided reaching in macaque posterior parietal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Dec;104(6):3494-509. doi: 10.1152/jn.01050.2009. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20844104 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed Spatial and Movement Representations in the Primate Posterior Parietal Cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 Mar 11;13:15. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00015. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 30914925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Basis of Touch and Proprioception in Primate Cortex.Compr Physiol. 2018 Sep 14;8(4):1575-1602. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c170033. Compr Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30215864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen RA, Buneo CA. Intentional maps in posterior parietal cortex. Ann Rev Neurosci 25: 189–220, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Andersen RA, Snyder LH, Bradley DC, Xing J. Multimodal representation of space in the posterior parietal cortex and its use in planning movements. Ann Rev Neurosci 20: 303–330, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Batista AP, Andersen RH. The parietal reach region codes the next planned movement in a sequential reach task. J Neurophysiol 85: 539–544, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Battaglia-Mayer A, Ferraina S, Mitsuda T, Marconi B, Genovesio A, Onorati P, Lacquaniti F, Caminiti R. Early coding of reaching in the parieto-occipital cortex. J Neurophysiol 83: 2374–2391, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Begliomini C, Wall MB, Smith AT, Castiello U. Differential cortical activity for precision and whole-hand visually guided grasping in humans. Eur J Neurosci 25: 1245–1252, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

