Mycoplasma genitalium-derived lipid-associated membrane proteins activate NF-kappaB through toll-like receptors 1, 2, and 6 and CD14 in a MyD88-dependent pathway
- PMID: 19793902
- PMCID: PMC2786392
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00281-09
Mycoplasma genitalium-derived lipid-associated membrane proteins activate NF-kappaB through toll-like receptors 1, 2, and 6 and CD14 in a MyD88-dependent pathway
Abstract
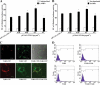
Mycoplasma genitalium is a leading pathogen of nongonoccocal chlamydia-negative urethritis, which has been implicated directly in numerous other genitourinary and extragenitourinary tract pathologies. The pathogenesis of infection is attributed in part to excessive immune responses. M. genitalium-derived lipid-associated membrane proteins (LAMPs) are a mixture of bacterial lipoproteins, exposed at the surface of mycoplasma, that are potent inducers of the host innate immune system. However, the interaction of M. genitalium-derived LAMPs as pathogenic agents with Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and the signaling pathways responsible for active inflammation and NF-kappaB activation have not been fully elucidated. In this study, LAMPs induced the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in a dose-dependent manner. Blocking assays showed that TLR2- and CD14-neutralizing antibodies reduced the expression of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in THP-1 cells. Furthermore, LAMP-induced NF-kappaB activation was increased in 293T cells transfected with TLR2 plasmid. The activity of NF-kappaB was synergically augmented by cotransfected TLR1, TLR6, and CD14. Additionally, LAMPs were shown to inhibit NF-kappaB expression by cotransfection with dominant-negative MyD88 and TLR2 plasmids. These results suggest that M. genitalium-derived LAMPs activate NF-kappaB via TLR1, TLR2, TLR6, and CD14 in a MyD88-dependent pathway.
Figures
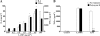




References
-
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675-680. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2004. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499-511. - PubMed
-
- Barton, G. M., and R. Medzhitov. 2003. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300:1524-1525. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. 2004. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430:257-263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

