Differential expression of two distinct functional isoforms of melanopsin (Opn4) in the mammalian retina
- PMID: 19793992
- PMCID: PMC2802713
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2036-09.2009
Differential expression of two distinct functional isoforms of melanopsin (Opn4) in the mammalian retina
Abstract
Melanopsin is the photopigment that confers photosensitivity to a subset of retinal ganglion cells (pRGCs) that regulate many non-image-forming tasks such as the detection of light for circadian entrainment. Recent studies have begun to subdivide the pRGCs on the basis of morphology and function, but the origin of these differences is not yet fully understood. Here we report the identification of two isoforms of melanopsin from the mouse Opn4 locus, a previously described long isoform (Opn4L) and a novel short isoform (Opn4S) that more closely resembles the sequence and structure of rat and human melanopsins. Both isoforms, Opn4L and Opn4S, are expressed in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, traffic to the plasma membrane and form a functional photopigment in vitro. Quantitative PCR revealed that Opn4S is 40 times more abundant than Opn4L. The two variants encode predicted proteins of 521 and 466 aa and only differ in the length of their C-terminal tails. Antibodies raised to isoform-specific epitopes identified two discrete populations of melanopsin-expressing RGCs, those that coexpress Opn4L and Opn4S and those that express Opn4L only. Recent evidence suggests that pRGCs show a range of anatomical subtypes, which may reflect the functional diversity reported for mouse Opn4-mediated light responses. The distinct isoforms of Opn4 described in this study provide a potential molecular basis for generating this diversity, and it seems likely that their differential expression plays a role in generating the variety of pRGC light responses found in the mammalian retina.
Figures

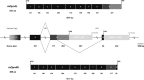




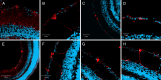

Comment in
-
New clues suggest distinct functional roles for M1 and M2 intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 3;30(5):1580-1. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5920-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20130168 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of melanopsin isoforms Opn4L and Opn4S during postnatal development of the mouse retina.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034531. Epub 2012 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496826 Free PMC article.
-
Isoforms of Melanopsin Mediate Different Behavioral Responses to Light.Curr Biol. 2015 Sep 21;25(18):2430-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.07.071. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26320947 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, localization and circadian expression of chicken melanopsin (Opn4): differential regulation of expression in pineal and retinal cell types.J Neurochem. 2005 Jan;92(1):158-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02874.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15606905
-
Melanopsin--shedding light on the elusive circadian photopigment.Chronobiol Int. 2004 Mar;21(2):189-204. doi: 10.1081/cbi-120037816. Chronobiol Int. 2004. PMID: 15332341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous expression of melanopsin: Present, problems and prospects.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 May;52:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26850932 Review.
Cited by
-
Sema6B, Sema6C, and Sema6D expression and function during mammalian retinal development.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e63207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063207. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23646199 Free PMC article.
-
Flp-recombinase mouse line for genetic manipulation of ipRGCs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 8:2024.05.06.592761. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.06.592761. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38766000 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Two Opsin 3-Related Proteins in the Chicken Retina and Brain: A TMT-Type Opsin 3 Is a Blue-Light Sensor in Retinal Horizontal Cells, Hypothalamus, and Cerebellum.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):e0163925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163925. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27861495 Free PMC article.
-
Light sensitivity in a vertebrate mechanoreceptor?J Exp Biol. 2015 Sep;218(Pt 18):2826-9. doi: 10.1242/jeb.125203. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26206352 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells: circuits and functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(3):889-907. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03641-5. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32965515 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baver SB, Pickard GE, Sollars PJ, Pickard GE. Two types of melanopsin retinal ganglion cell differentially innervate the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus and the olivary pretectal nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:1763–1770. - PubMed
-
- Belenky MA, Smeraski CA, Provencio I, Sollars PJ, Pickard GE. Melanopsin retinal ganglion cells receive bipolar and amacrine cell synapses. J Comp Neurol. 2003;460:380–393. - PubMed
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002;295:1070–1073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
