The ABC transporter PXA1 and peroxisomal beta-oxidation are vital for metabolism in mature leaves of Arabidopsis during extended darkness
- PMID: 19794119
- PMCID: PMC2768912
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.064857
The ABC transporter PXA1 and peroxisomal beta-oxidation are vital for metabolism in mature leaves of Arabidopsis during extended darkness
Abstract
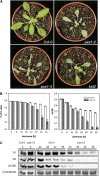
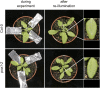
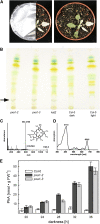
Fatty acid beta-oxidation is essential for seedling establishment of oilseed plants, but little is known about its role in leaf metabolism of adult plants. Arabidopsis thaliana plants with loss-of-function mutations in the peroxisomal ABC-transporter1 (PXA1) or the core beta-oxidation enzyme keto-acyl-thiolase 2 (KAT2) have impaired peroxisomal beta-oxidation. pxa1 and kat2 plants developed severe leaf necrosis, bleached rapidly when returned to light, and died after extended dark treatment, whereas the wild type was unaffected. Dark-treated pxa1 plants showed a decrease in photosystem II efficiency early on and accumulation of free fatty acids, mostly alpha-linolenic acid [18:3(n-3)] and pheophorbide a, a phototoxic chlorophyll catabolite causing the rapid bleaching. Isolated wild-type and pxa1 chloroplasts challenged with comparable alpha-linolenic acid concentrations both showed an 80% reduction in photosynthetic electron transport, whereas intact pxa1 plants were more susceptible to the toxic effects of alpha-linolenic acid than the wild type. Furthermore, starch-free mutants with impaired PXA1 function showed the phenotype more quickly, indicating a link between energy metabolism and beta-oxidation. We conclude that the accumulation of free polyunsaturated fatty acids causes membrane damage in pxa1 and kat2 plants and propose a model in which fatty acid respiration via peroxisomal beta-oxidation plays a major role in dark-treated plants after depletion of starch reserves.
Figures





Comment in
-
Nocturnal energy demand in plants: insights from studying mutants impaired in β-oxidation.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jul;5(7):842-4. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.7.11821. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20505361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adham, A.R., Zolman, B.K., Millius, A., and Bartel, B. (2005). Mutations in Arabidopsis acyl-CoA oxidase genes reveal distinct and overlapping roles in beta-oxidation. Plant J. 41 859–874. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Baker, A., Graham, I.A., Holdsworth, M., Smith, S.M., and Theodoulou, F.L. (2006). Chewing the fat: Beta-oxidation in signalling and development. Trends Plant Sci. 11 124–132. - PubMed
-
- Berger, J., and Gärtner, J. (2006). X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: Clinical, biochemical and pathogenetic aspects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763 1721–1732. - PubMed
-
- Bligh, E.G., and Dyer, W.J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37 911–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

