Context representations, context functions, and the parahippocampal-hippocampal system
- PMID: 19794181
- PMCID: PMC2769166
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1494409
Context representations, context functions, and the parahippocampal-hippocampal system
Abstract
Psychologists and neurobiologists have a long-standing interest in understanding how the context surrounding the events of our lives is represented and how it influences our behavior. The hippocampal formation emerged very early as a major contributor to how context is represented and functions. There is a large literature examining its contribution that on the surface reveals an array of conflicting outcomes and controversy. This review reveals that these conflicts can be resolved by building Nadel and Willner's dual-process theory of context representations. Two general conclusions emerge: (1) There are two neural systems that can support context representations and functions-a neocortical system composed primarily of perirhinal and postrhinal cortices and a hippocampal system that includes perirhinal, postrhinal, entorhinal cortices, and the hippocampal formation. (2) These two systems are not equivalent-some context representations and functions are uniquely supported by the hippocampal system. These conclusions are discussed in the context of canonical ideas about the special properties of the hippocampal system that enable it to make unique contributions to memory.
Figures

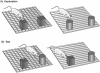
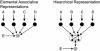
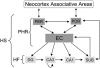
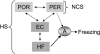
Similar articles
-
Beyond the hippocampus: The role of parahippocampal-prefrontal communication in context-modulated behavior.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021 Nov;185:107520. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107520. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 34537379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional neuroanatomy of the parahippocampal region in the rat: the perirhinal and postrhinal cortices.Hippocampus. 2007;17(9):709-22. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20314. Hippocampus. 2007. PMID: 17604355 Review.
-
The parahippocampal region: corticocortical connectivity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000 Jun;911:25-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06717.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 10911865 Review.
-
Corticohippocampal contributions to spatial and contextual learning.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 14;24(15):3826-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0410-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15084664 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal connections between the amygdala and the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, and postrhinal cortex in rat. A review.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000 Jun;911:369-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06738.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 10911886 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating and fragmenting memories under stress and alcohol.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Feb 8;30:100615. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100615. eCollection 2024 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38375503 Free PMC article.
-
Retrosplenial cortex damage produces retrograde and anterograde context amnesia using strong fear conditioning procedures.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Sep 2;369:111920. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111920. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31039379 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Flexibility of Systems Consolidation and the Synaptic Occupancy/Reset Theory (SORT): Cues About the Nature of the Engram.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019 Feb 13;11:1. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00001. eCollection 2019. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30814946 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive neural responses to pain stimuli during induced sadness in patients with somatoform pain disorder: An fMRI study.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 Jun 12;2:782-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.06.001. eCollection 2013. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24179828 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny and neural substrates of the context preexposure facilitation effect.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011 Feb;95(2):190-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.11.011. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21129493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Keen S, Warburton EC, Bussey TJ. Extensive cytotoxic lesions involving both the rhinal cortices and area TE impair recognition but spare spatial alternation in the rat. Brain Res. 1997;43:279–287. - PubMed
-
- Antoniadis EA, McDonald RJ. Amygdala, hippocampus, and discrimination fear conditioning to context. Behav Brain Res. 2000;108:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Ayres JJ, Bombace JC, Shurtleff D, Vigorito M. Conditioned suppression tests of the context-blocking hypothesis: Testing in the absence of the preconditioned context. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1985;1:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Balsam PD, Tomie A. Context and learning. Erlbaum Associates; Hilldsale, NJ: 1985.
-
- Bannerman DM, Yee BK, Good MA, Heupel MJ, Iversen SD, Rawlins JN. Double dissociation of function within the hippocampus: A comparison of dorsal, ventral, and complete hippocampal cytotoxic lesions. Behav Neurosci. 1999;113:1170–1188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
