Age-related impairments of new memories reflect failures of learning, not retention
- PMID: 19794183
- PMCID: PMC2769163
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1503209
Age-related impairments of new memories reflect failures of learning, not retention
Abstract
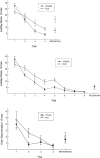
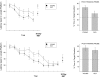
Learning impairments and the instability of memory are defining characteristics of cognitive aging. However, it is unclear if deficits in the expression of new memories reflect an accelerated decay of the target memory or a consequence of inefficient learning. Here, aged mice (19-21-mo old) exhibited acquisition deficits (relative to 3-5-mo old mice) on three learning tasks, although these deficits were overcome with additional training. When tested after a 30-d retention interval, the performance of aged animals was impaired if initial learning had been incomplete. However, if trained to equivalent levels of competence, aged animals exhibited no retention deficits relative to their young counterparts. These results suggest that age-related "memory" impairments can be overcome through a more effective learning regimen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal attentional engagement rescues mice from age-related cognitive declines and cognitive inflexibility.Learn Mem. 2011 Apr 26;18(5):345-56. doi: 10.1101/lm.2034711. Print 2011. Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21521768 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related declines in general cognitive abilities of Balb/C mice are associated with disparities in working memory, body weight, and general activity.Learn Mem. 2008 Oct 2;15(10):733-46. doi: 10.1101/lm.954808. Print 2008 Oct. Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 18832560 Free PMC article.
-
The aged mouse as a model of cognitive decline with special emphasis on studies in NMRI mice.Behav Brain Res. 1993 Nov 30;57(2):163-73. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(93)90132-a. Behav Brain Res. 1993. PMID: 8117421 Review.
-
Mimicking Age-Associated Gadd45γ Dysregulation Results in Memory Impairments in Young Adult Mice.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 5;40(6):1197-1210. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1621-19.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 11. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31826946 Free PMC article.
-
Learning and memory in the SAMP8 mouse.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1998;22(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(96)00063-2. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1998. PMID: 9491937 Review.
Cited by
-
Triangular relationship between sleep spindle activity, general cognitive ability and the efficiency of declarative learning.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049561. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185361 Free PMC article.
-
New neurons in an aged brain.Behav Brain Res. 2012 Feb 14;227(2):497-507. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.10.009. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Behav Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22024433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal attentional engagement rescues mice from age-related cognitive declines and cognitive inflexibility.Learn Mem. 2011 Apr 26;18(5):345-56. doi: 10.1101/lm.2034711. Print 2011. Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21521768 Free PMC article.
-
The paradox of intelligence: Heritability and malleability coexist in hidden gene-environment interplay.Psychol Bull. 2018 Jan;144(1):26-47. doi: 10.1037/bul0000131. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Psychol Bull. 2018. PMID: 29083200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes CA, McNaughton CL. An age comparison of the rates of acquisition and forgetting of spatial information in relation to long-term enhancement of hippocampal synapses. Behav Neurosci. 1985;99:1040–1048. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BA. In: Early behavior: Comparative and developmental approaches. Stevenson HW, et al., editors. Wiley; New York: 1967.
-
- Campbell BA, Jaynes J. Reinstatement. Psychol Rev. 1966;73:478–480. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BA, Spear NE. Ontogeny of memory. Psychol Rev. 1972;79:215–236. - PubMed
-
- Gage FH, Dunnett SSBA. Spatial learning and motor deficits in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging. 1984;5:43–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
