Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 19794443
- PMCID: PMC3021468
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2875
Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
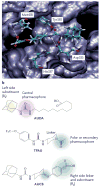
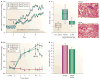
The cardiovascular effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) include vasodilation, antimigratory actions on vascular smooth muscle cells and anti-inflammatory actions. These endogenous lipid mediators are broken down into diols by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), and so inhibiting this enzyme would be expected to enhance the beneficial cardiovascular properties of EETs. sEH inhibitors (sEHIs) that are based on 1,3-disubstituted urea have been rapidly developed, and have been shown to be antihypertensive and anti-inflammatory, and to protect the brain, heart and kidney from damage. Although challenges for the future exist - including improving the drug-like properties of sEHIs and finding better ways to target sEHIs to specific tissues - the recent initiation of the first clinical trials of sEHIs has highlighted the therapeutic potential of these agents.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzgerald GA. Coxibs and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1709–11. - PubMed
-
- Puri A, McGoon MD, Kushwaha SS. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: current therapeutic strategies. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4:319–29. - PubMed
-
- Steiropoulos P, Trakada G, Bouros D. Current pharmacological treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2008;3:11–9. - PubMed
-
- Braden GL, O’Shea MH, Mulhern JG, Germain MJ. Acute renal failure and hyperkalaemia associated with cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:1149–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

