Cone beam micro-CT system for small animal imaging and performance evaluation
- PMID: 19794829
- PMCID: PMC2754077
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/960573
Cone beam micro-CT system for small animal imaging and performance evaluation
Abstract
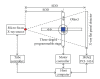
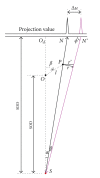
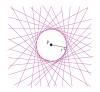
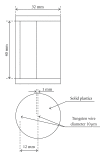
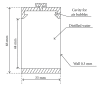
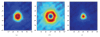
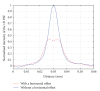
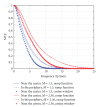
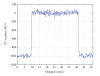
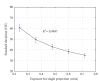
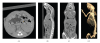
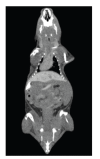
A prototype cone-beam micro-CT system for small animal imaging has been developed by our group recently, which consists of a microfocus X-ray source, a three-dimensional programmable stage with object holder, and a flat-panel X-ray detector. It has a large field of view (FOV), which can acquire the whole body imaging of a normal-size mouse in a single scan which usually takes about several minutes or tens of minutes. FDK method is adopted for 3D reconstruction with Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) acceleration. In order to reconstruct images with high spatial resolution and low artifacts, raw data preprocessing and geometry calibration are implemented before reconstruction. A method which utilizes a wire phantom to estimate the residual horizontal offset of the detector is proposed, and 1D point spread function is used to assess the performance of geometric calibration quantitatively. System spatial resolution, image uniformity and noise, and low contrast resolution have been studied. Mouse images with and without contrast agent are illuminated in this paper. Experimental results show that the system is suitable for small animal imaging and is adequate to provide high-resolution anatomic information for bioluminescence tomography to build a dual modality system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accurate technique for complete geometric calibration of cone-beam computed tomography systems.Med Phys. 2005 Apr;32(4):968-83. doi: 10.1118/1.1869652. Med Phys. 2005. PMID: 15895580
-
ALBIRA: a small animal PET∕SPECT∕CT imaging system.Med Phys. 2013 May;40(5):051906. doi: 10.1118/1.4800798. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23635276
-
Flat-panel cone-beam computed tomography for image-guided radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Aug 1;53(5):1337-49. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)02884-5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 12128137
-
A prototype table-top inverse-geometry volumetric CT system.Med Phys. 2006 Jun;33(6):1867-78. doi: 10.1118/1.2192887. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16872094
-
Fast and effective single-scan dual-energy cone-beam CT reconstruction and decomposition denoising based on dual-energy vectorization.Med Phys. 2021 Sep;48(9):4843-4856. doi: 10.1002/mp.15117. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34289129
Cited by
-
Quantifying the gantry sag on linear accelerators and introducing an MLC-based compensation strategy.Med Phys. 2012 Apr;39(4):2156-62. doi: 10.1118/1.3697528. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22482636 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution computed tomography of single breast cancer microcalcifications in vivo.Mol Imaging. 2011 Aug;10(4):295-304. doi: 10.2310/7290.2010.00050. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21504703 Free PMC article.
-
Cone Beam X-ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Based on Bayesian Method.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2017 Jan;36(1):225-235. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2603843. Epub 2016 Aug 26. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27576245 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of the anti-angiogenic and anti-neoplastic effects of Endostar on liver cancer through optical molecular imaging.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 8;9(1):e85559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085559. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416426 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and Robust Reconstruction for Fluorescence Molecular Tomography via L1-2 Regularization.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5065217. doi: 10.1155/2016/5065217. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28050563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cherry SR. In vivo molecular and genomic imaging: new challenges for imaging physics. Physics in Medical and Biology. 2004;49(3):R13–R48. - PubMed
-
- Holdsworth DW, Drangova M, Fenster A. A high-resolution XRII-based quantitative volume CT scanner. Medical Physics. 1993;20(2):449–462. - PubMed
-
- Paulus MJ, Sari-Sarraf H, Gleason SS, et al. A new X-ray computed tomography system for laboratory mouse imaging. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 1999;46(3):558–564.
-
- Rossi M, Casali F, Bettuzzi M, et al. Experimental micro-CT system for X-ray NDT. In: Developments in X-Ray Tomography III, vol. 4503; August 2001; San Diego, Calif, USA. pp. 338–348. Proceedings of the SPIE.
-
- Lee SC, Kim HK, Chun IK, Cho MH, Lee SY, Cho MH. A flat-panel detector based micro-CT system: performance evaluation for small-animal imaging. Physics in Medical and Biology. 2003;48(24):4173–4185. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

