Switches in nutrient and inositol signaling
- PMID: 19794846
- PMCID: PMC2664490
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.4.4.8063
Switches in nutrient and inositol signaling
Abstract
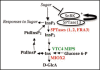
Studies of signal transduction networks such as the inositol signaling pathway can provide important insights for our understanding of the regulation of various biological events, including growth and development, disease and stress responses. Recently, we have identified a myo-inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (5PTase13, At1g05630) that hydrolyzes the second messenger inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3] and also interacts with the sucrose nonfermenting-1-related kinase (SnRK1.1) in the yeast two hybrid system and in vitro. Plant SnRK1 proteins coordinate nutrient and developmental signals to regulate plant survival under stress, darkness and sugar deprivation conditions. Using mutants defective in 5PTase13, we showed that 5PTase13 can act as a regulator of SnRK1 activity, and that regulation differs with nutrient availability. Specifically, we showed that 5PTase13 acts as a positive regulator of SnRK1 activity by preventing SnRK1.1 from proteasomal degradation in the presence of low nutrients or 6% glucose. In contrast, under severe starvation conditions, 5PTase13 acts as a negative regulator of SnRK1 activity. We present here a model of 5PTase13 regulatory interaction with SnRK1.1 and further discuss its importance for balancing inositol signaling and metabolism.
Keywords: 5PTase13; PRL; SnRK1; WD40 proteins; inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3]; myo-inositol.
Figures

Comment on
-
Interaction of the WD40 domain of a myoinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase with SnRK1 links inositol, sugar, and stress signaling.Plant Physiol. 2008 Dec;148(4):1868-82. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130575. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18931139 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Interaction of the WD40 domain of a myoinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase with SnRK1 links inositol, sugar, and stress signaling.Plant Physiol. 2008 Dec;148(4):1868-82. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130575. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18931139 Free PMC article.
-
Enantiomers of myo-inositol-1,3,4-trisphosphate and myo-inositol-1,4,6 -trisphosphate: stereospecific recognition by cerebellar and platelet myo-inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Nov;50(5):1223-30. Mol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8913354
-
Molecular recognition at the myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. 3-position substituted myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate analogues reveal the binding and Ca2+ release requirements for high affinity interaction with the myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor.J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26815-21. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7929418
-
The pathway of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate phosphorylation in liver. Identification of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 6-kinase, myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5-kinase, and myo-inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate 5-kinase.J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19879-86. J Biol Chem. 1989. PMID: 2584198
-
Inositol polyphosphates and intracellular calcium release.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 15;273(1):1-15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90156-2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989. PMID: 2667466 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutral invertase, hexokinase and mitochondrial ROS homeostasis: emerging links between sugar metabolism, sugar signaling and ascorbate synthesis.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Oct;6(10):1567-73. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.10.17036. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21918379 Free PMC article.
-
New aspects of Phloem-mediated long-distance lipid signaling in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Mar 28;3:53. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00053. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22639651 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of lipids and lipid-binding proteins in phloem exudates from Arabidopsis thaliana.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jun;63(10):3603-16. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers028. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22442409 Free PMC article.
-
Seed Biofortification and Phytic Acid Reduction: A Conflict of Interest for the Plant?Plants (Basel). 2015 Nov 20;4(4):728-55. doi: 10.3390/plants4040728. Plants (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27135349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vucenik I, Shamsuddin AM. Protection against cancer by dietary IP6 and inositol. Nutr Cancer. 2006;55:109–125. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium oscillations. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 in press. - PubMed
-
- Astle MV, Horan KA, Ooms LM, Mitchell CA. The inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases: traffic controllers, waistline watchers and tumour suppressors? Biochem Soc Symp. 2007:161–181. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
