Decorin suppresses prostate tumor growth through inhibition of epidermal growth factor and androgen receptor pathways
- PMID: 19794963
- PMCID: PMC2745670
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.09760
Decorin suppresses prostate tumor growth through inhibition of epidermal growth factor and androgen receptor pathways
Abstract
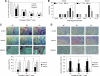
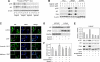
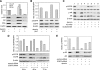
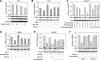
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and androgen receptor (AR) pathways play pivotal roles in prostate cancer progression. Therefore, agents with dual-targeting ability may have important therapeutic potential. Decorin, a proteoglycan present in the tumor microenvironment, is known to regulate matrix assembly, growth factor binding, and receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Here, we show that in prostate-specific Pten(P-/-) mice, a genetically defined, immune-competent mouse model of prostate cancer, systemic delivery of decorin inhibits tumor progression by targeting cell proliferation and survival pathways. Moreover, in human prostate cancer cells, we show that decorin specifically inhibits EGFR and AR phosphorylation and cross talk between these pathways. This prevents AR nuclear translocation and inhibits the production of prostate specific antigen. Further, the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt cell survival pathway is suppressed leading to tumor cell apoptosis. Those findings highlight the effectiveness of decorin in the presence of a powerful genetic cancer risk and implicate decorin as a potential new agent for prostate cancer therapy by targeting EGFR/AR-PI3K-Akt pathways.
Figures



References
-
- Mimeault M, Batra SK. Recent advances on multiple tumorigenic cascades involved in prostatic cancer progression and targeting therapies. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Chung LW, Baseman A, Assikis V, Zhau HE. Molecular insights into prostate cancer progression: the missing link of tumor microenvironment. J Urol. 2005;173:10–20. - PubMed
-
- Ferdous Z, Wei VM, Iozzo R, Hook M, Grande-Allen KJ. Decorin-transforming growth factor-interaction regulates matrix organization and mechanical characteristics of three-dimensional collagen matrices. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:35887–35898. - PubMed
-
- Järveläinen H, Puolakkainen P, Pakkanen S, Brown EL, Höök M, Iozzo RV, Sage EH, Wight TN. A role for decorin in cutaneous wound healing and angiogenesis. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14:443–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
