Tumor-endothelium cross talk blocks recruitment of neutrophils to endothelial cells: a novel mechanism of endothelial cell anergy
- PMID: 19794964
- PMCID: PMC2745671
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.09762
Tumor-endothelium cross talk blocks recruitment of neutrophils to endothelial cells: a novel mechanism of endothelial cell anergy
Abstract
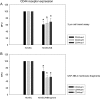
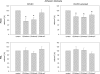
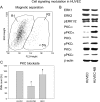
Tumor cells have evolved effective strategies to escape the host immune response. The objective of this study was to determine whether tumor cells can condition endothelial cells in a specific manner to prevent subsequent adhesion of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and/or peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and UKF-NB-4 neuroblastoma tumor cells were established in coculture on opposite sides of porous transwell filters. After 24 hours with and without HUVEC conditioning, PMNs or PBLs were added to the HUVEC monolayer. Adhesion to conditioned HUVEC versus adhesion to nonconditioned HUVEC was compared. Effects on endothelial CD44v4, CD44v5, CD44v7, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), E-selectin, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) adhesion receptor expression were analyzed by flow cytometry, intracellular signaling proteins of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and protein kinase C (PKC) subtypes quantified by Western blot analysis. Endothelial conditioning led to a distinct reduction in PMN but not in PBL adhesion to HUVEC. CD44 was significantly reduced, whereas ICAM-1, E-selectin, and VCAM-1 were not altered during HUVEC conditioning. Antibody blockade against CD44v4, CD44v5, and CD44v7 inhibited PMN but not PBL binding. The observed effects were caused by direct tumor cell-HUVEC contact because addition of isolated tumor cell membrane fragments but not of soluble cell culture supernatant to HUVEC induced the CD44 receptor loss. PKCalpha activity was strongly enhanced in conditioned HUVEC. Blocking PKC prevented the reduction in PMN binding, indicating that this protein is involved in PMN adhesion regulation. A novel tumor escape strategy is presented here. Cell contact-dependent adhesion of tumor cells to the vascular wall promotes down-regulation of endothelial CD44 receptor expression, impairing an effective neutrophil attack.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Renal cell carcinoma alters endothelial receptor expression responsible for leukocyte adhesion.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):20410-24. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7804. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943029 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma upregulates ICAM-1 expression on endothelial cells through engagement of tumor CD44 with endothelial E-selectin and activation of a PKCα-p38-SP-1 pathway.FASEB J. 2014 Nov;28(11):4591-609. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-202747. Epub 2014 Aug 19. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 25138157 Free PMC article.
-
Ibuprofen inhibits pyrogen-dependent expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 on human endothelial cells.Life Sci. 1996;58(23):2167-81. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(96)00210-x. Life Sci. 1996. PMID: 8649201
-
Activation of human endothelial cells by mobilized porcine leukocytes in vitro: implications for mixed chimerism in xenotransplantation.Transplantation. 2002 Apr 27;73(8):1302-9. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200204270-00020. Transplantation. 2002. PMID: 11981426
-
S. aureus and E. coli change the force and work of adhesion between P- and E-selectins of endothelial cells and ligands of neutrophil granulocytes.Micron. 2021 Nov;150:103139. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2021.103139. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Micron. 2021. PMID: 34428610 Review.
Cited by
-
The interconnectedness of cancer cell signaling.Neoplasia. 2011 Dec;13(12):1183-93. doi: 10.1593/neo.111746. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 22241964 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA GAPLINC promotes angiogenesis by regulating miR-211 under hypoxia in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):8090-8100. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14678. Epub 2019 Oct 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31589383 Free PMC article.
-
Renal cell carcinoma alters endothelial receptor expression responsible for leukocyte adhesion.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):20410-24. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7804. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943029 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the myeloid microenvironment in neuroblastoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 13;42(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02913-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38087370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dinosaurs and ancient civilizations: reflections on the treatment of cancer.Neoplasia. 2010 Dec;12(12):957-68. doi: 10.1593/neo.101588. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 21170260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Igney FH, Krammer PH. Immune escape of tumors: apoptosis resistance and tumor counterattack. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71:907–920. - PubMed
-
- Di Carlo E, Forni G, Lollini P, Colombo MP, Modesti A, Musiani P. The intriguing role of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in antitumor reactions. Blood. 2001;97:339–345. - PubMed
-
- Jackaman C, Lew AM, Zhan Y, Allan JE, Koloska B, Graham PT, Robinson BW, Nelson DJ. Deliberately provoking local inflammation drives tumors to become their own protective vaccine site. Int Immunol. 2008;20:1467–1479. - PubMed
-
- Halapi E. Oligoclonal T cells in human cancer. Med Oncol. 1998;15:203–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
