Clinical implications of KRAS mutations in lung cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: an important role for mutations in minor clones
- PMID: 19794967
- PMCID: PMC2745674
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.09814
Clinical implications of KRAS mutations in lung cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: an important role for mutations in minor clones
Abstract
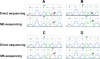
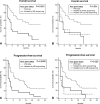
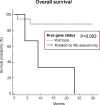
Mutations inducing resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy may have a clinical impact even if present in minor cell clones which could expand during treatment. We tested this hypothesis in lung cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Eighty-three patients with lung adenocarcinoma treated with erlotinib or gefitinib were included in this study. The mutational status of KRAS and EGFR was investigated by direct sequencing (DS). KRAS mutations were also assessed by mutant-enriched sequencing (ME-sequencing). DS detected KRAS mutations in 16 (19%) of 83 tumors; ME-sequencing identified all the mutations detected by DS but also mutations in minor clones of 14 additional tumors, for a total of 30 (36%) of 83. KRAS mutations assessed by DS and ME-sequencing significantly correlated with resistance to TKIs (P = .04 and P = .004, respectively) and significantly affected progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). However, the predictive power of mutations assessed by ME-sequencing was higher than that obtained by DS (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.82, P = .0001 vs HR = 1.98, P = .04, respectively, for OS; HR = 2.52, P = .0005 vs HR = 2.21, P = .007, respectively, for PFS). Survival outcome of patients harboring KRAS mutations in minor clones, detected only by ME-sequencing, did not differ from that of patients with KRAS mutations detected by DS. Only KRAS mutations assessed by ME-sequencing remained an independent predictive factor at multivariate analysis. KRAS mutations in minor clones have an important impact on response and survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR-TKI. The use of sensitive detection methods could allow to more effectively identify treatment-resistant patients.
Figures



References
-
- Mendelsohn J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(Suppl 18):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S, Rischin D, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2237–2246. - PubMed
-
- Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2149–2158. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
