The relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity and complement 1 inhibitor
- PMID: 19794979
- PMCID: PMC2752764
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.831
The relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity and complement 1 inhibitor
Abstract
Complement 1 (C1) inhibitor is an acute phase protein with anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV), the parameter of arterial stiffness, and C1 inhibitor. One hundred subjects were randomly enrolled in this study. Data about baPWV, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, and body mass index (BMI) were measured. Blood tests for total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein, high density lipoprotein, triglycerides, hemoglobin A1c, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, complement 3, and C1 inhibitor were performed. Based on the Pearson correlation, the C1 inhibitor showed a positive relation to the baPWV (P<0.001). Multiple regression analysis revealed the significant predictors of baPWV were not only the conventional risk factors of arteriosclerosis and/or atherosclerosis, such as age (P<0.001), gender (P<0.001), hypertension (P<0.001), and BMI (P=0.006), but also the acute phase protein, C1 inhibitor (P=0.025). In conclusion, C1 inhibitor is associated with arterial stiffness through its association with increased inflammation.
Keywords: Complement 1 Inhibitor; Pulse Wave Velocity; Stiffness.
Figures
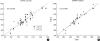
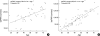
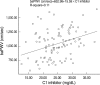
Similar articles
-
Correlation between brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and arterial compliance and cardiovascular risk factors in elderly patients with arteriosclerosis.Hypertens Res. 2006 May;29(5):309-14. doi: 10.1291/hypres.29.309. Hypertens Res. 2006. PMID: 16832150
-
[Relationship between radial augmentation index and other indices for evaluating arteriosclerosis].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Dec 18;45(6):916-22. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 24343074 Chinese.
-
Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: an index of central arterial stiffness?J Hum Hypertens. 2005 May;19(5):401-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1001838. J Hum Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 15729378
-
Brachio-ankle pulse wave velocity and cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI).Biomed Pharmacother. 2004 Oct;58 Suppl 1:S95-8. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(04)80015-5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15754845 Review.
-
Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in the measurement of arterial stiffness: recent evidence and clinical applications.Curr Hypertens Rev. 2014;10(1):49-57. doi: 10.2174/157340211001141111160957. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2014. PMID: 25392144 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in normotensive young adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Nov;27(11):1359-63. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1359. Epub 2012 Oct 30. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23166418 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Standard Protocol for the Harmonic Analysis of Radial Pulse Wave and Assessing Its Reliability in Healthy Humans.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2015 Oct 14;3:2900206. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2015.2490661. eCollection 2015. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2015. PMID: 27170904 Free PMC article.
-
Pitfalls in the ankle-brachial index and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018 Apr 3;14:41-62. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S159437. eCollection 2018. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29662315 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular stiffening in pulmonary hypertension: cause or consequence? (2013 Grover Conference series).Pulm Circ. 2014 Dec;4(4):560-80. doi: 10.1086/677370. Pulm Circ. 2014. PMID: 25610594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zanker KS. General introduction to innate immunity: Dr. Jekyl/Mr. Hyde quality of the innate immune system. Contrib Microbiol. 2008;15:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Caliezi C, Wuillemin WA, Zeerleder S, Redondo M, Eisele B, Hack CE. C1-Esterase inhibitor: an anti-inflammatory agent and its potential use in the treatment of diseases other than hereditary angioedema. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:91–112. - PubMed
-
- Kalter ES, Daha MR, ten Cate JW, Verhoef J, Bouma BN. Activation and inhibition of Hageman factor-dependent pathways and the complement system in uncomplicated bacteremia or bacterial shock. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Kostner KM, Fahti RB, Case C, Hobson P, Tate J, Marwick TH. Inflammation, complement activation and endothelial function in stable and unstable coronary artery disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;365:129–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

