The relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity and complement 1 inhibitor
- PMID: 19794979
- PMCID: PMC2752764
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.831
The relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity and complement 1 inhibitor
Abstract
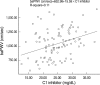
Complement 1 (C1) inhibitor is an acute phase protein with anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the relationship between brachial ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV), the parameter of arterial stiffness, and C1 inhibitor. One hundred subjects were randomly enrolled in this study. Data about baPWV, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, and body mass index (BMI) were measured. Blood tests for total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein, high density lipoprotein, triglycerides, hemoglobin A1c, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, complement 3, and C1 inhibitor were performed. Based on the Pearson correlation, the C1 inhibitor showed a positive relation to the baPWV (P<0.001). Multiple regression analysis revealed the significant predictors of baPWV were not only the conventional risk factors of arteriosclerosis and/or atherosclerosis, such as age (P<0.001), gender (P<0.001), hypertension (P<0.001), and BMI (P=0.006), but also the acute phase protein, C1 inhibitor (P=0.025). In conclusion, C1 inhibitor is associated with arterial stiffness through its association with increased inflammation.
Keywords: Complement 1 Inhibitor; Pulse Wave Velocity; Stiffness.
Figures
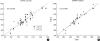
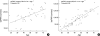
References
-
- Zanker KS. General introduction to innate immunity: Dr. Jekyl/Mr. Hyde quality of the innate immune system. Contrib Microbiol. 2008;15:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Caliezi C, Wuillemin WA, Zeerleder S, Redondo M, Eisele B, Hack CE. C1-Esterase inhibitor: an anti-inflammatory agent and its potential use in the treatment of diseases other than hereditary angioedema. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:91–112. - PubMed
-
- Kalter ES, Daha MR, ten Cate JW, Verhoef J, Bouma BN. Activation and inhibition of Hageman factor-dependent pathways and the complement system in uncomplicated bacteremia or bacterial shock. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Kostner KM, Fahti RB, Case C, Hobson P, Tate J, Marwick TH. Inflammation, complement activation and endothelial function in stable and unstable coronary artery disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;365:129–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

