Intrinsic amino acid side-chain hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity coefficients determined by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of model peptides: comparison with other hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity scales
- PMID: 19795449
- PMCID: PMC2792893
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.21316
Intrinsic amino acid side-chain hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity coefficients determined by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of model peptides: comparison with other hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity scales
Abstract
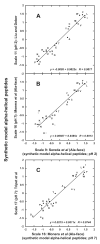
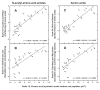
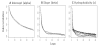
An accurate determination of the intrinsic hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of amino acid side-chains in peptides and proteins is fundamental in understanding many area of research, including protein folding and stability, peptide and protein function, protein-protein interactions and peptide/protein oligomerization, as well as the design of protocols for purification and characterization of peptides and proteins. Our definition of intrinsic hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of side-chains is the maximum possible hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of side-chains in the absence of any nearest-neighbor effects and/or any conformational effects of the polypeptide chain that prevent full expression of side-chain hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity. In this review, we have compared an experimentally derived intrinsic side-chain hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity scale generated from RP-HPLC retention behavior of de novo designed synthetic model peptides at pH 2 and pH 7 with other RP-HPLC-derived scales, as well as scales generated from classic experimental and calculation-based methods of octanol/water partitioning of Nalpha-acetyl-amino-acid amides or free energy of transfer of free amino acids. Generally poor correlation was found with previous RP-HPLC-derived scales, likely due to the random nature of the peptide mixtures in terms of varying peptide size, conformation and frequency of particular amino acids. In addition, generally poor correlation with the classical approaches served to underline the importance of the presence of a polypeptide backbone when generating intrinsic values. We have shown that the intrinsic scale determined here is in full agreement with the structural characteristics of amino acid side-chains.
Copyright 2009 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



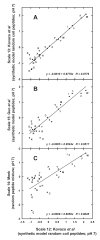
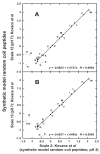

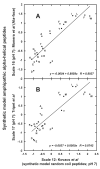

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

