Defective plasmacytoid dendritic cell-NK cell cross-talk in HIV infection
- PMID: 19795986
- PMCID: PMC2828160
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2008.0311
Defective plasmacytoid dendritic cell-NK cell cross-talk in HIV infection
Abstract
HIV viremia is associated with a wide range of immune dysfunctions that contribute to the immunocompromised state. HIV viremia has been shown to have a broad effect on several immune cell types and/or their interactions that are vital for mounting an effective immune response. In this study, we investigated the integrity of plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC)-NK cell interactions among HIV viremic, aviremic, and seronegative individuals. We describe a critical defect in the ability of pDCs from HIV-infected individuals to secrete IFN-alpha and TNF and subsequently activate NK cells. We also describe an inherent defect on NK cells from HIV-infected individuals to respond to pDC-secreted cytokines. Furthermore, we were able to demonstrate a direct effect of HIV trimeric gp120 on NK cells in vitro similar to that described ex vivo. Finally, we were able to establish that the HIV gp120-mediated suppressive effect on NK cells was a result of its binding to the integrin alpha(4)beta(7) expressed on NK cells. These findings suggest a novel mechanism by which HIV is capable of suppressing an innate immune function in infected individuals.
Figures
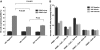
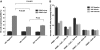
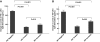
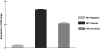
References
-
- Smyth MJ. Godfrey DI. Trapani JA. A fresh look at tumor immunosurveillance and immunotherapy. Nat immunol. 2001;2(4):293–299. - PubMed
-
- Long EO. Regulation of immune responses through inhibitory receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:875–904. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. On guard—activating NK cell receptors. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(1):23–27. - PubMed
-
- Moretta A. Bottino C. Vitale M, et al. Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:197–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

