Broadband plasmon waveguide resonance spectroscopy for probing biological thin films
- PMID: 19796490
- PMCID: PMC2912159
- DOI: 10.1366/000370209789379295
Broadband plasmon waveguide resonance spectroscopy for probing biological thin films
Abstract
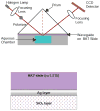
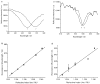
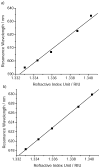
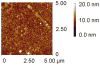
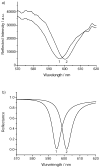
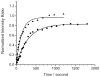
A commercially available spectrometer has been modified to perform plasmon waveguide resonance (PWR) spectroscopy over a broad spectral bandwidth. When compared to surface plasmon resonance (SPR), PWR has the advantage of allowing measurements in both s- and p-polarizations on a waveguide surface that is silica or glass rather than a noble metal. Here the waveguide is a BK7 glass slide coated with silver and silica layers. The resonance wavelength is sensitive to the optical thickness of the medium adjacent to the silica layer. The sensitivity of this technique is characterized and compared with broadband SPR both experimentally and theoretically. The sensitivity of spectral PWR is comparable to that of spectral SPR for samples with refractive indices close to that of water. The hydrophilic surface of the waveguide allows supported lipid bilayers to be formed spontaneously by vesicle fusion; in contrast, the surface of an SPR chip requires chemical modification to create a supported lipid membrane. Broadband PWR spectroscopy should be a useful technique to study biointerfaces, including ligand binding to transmembrane receptors and adsorption of peripheral proteins on ligand-bearing membranes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasmon-waveguide resonance spectroscopy studies of lateral segregation in solid-supported proteolipid bilayers.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;398:159-78. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-513-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18214380
-
Study of G-Protein Coupled Receptor Signaling in Membrane Environment by Plasmon Waveguide Resonance.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Apr 16;52(4):1059-1067. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00007. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30865424
-
Coupled plasmon-waveguide resonators: a new spectroscopic tool for probing proteolipid film structure and properties.Biophys J. 1997 Nov;73(5):2791-7. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78308-5. Biophys J. 1997. PMID: 9370473 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmon resonance methods in GPCR signaling and other membrane events.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005 Aug;6(4):293-312. doi: 10.2174/1389203054546352. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005. PMID: 16101432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the molecular mechanisms of biomembrane structural changes and interactions by optical biosensor technology.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1848(9):1868-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26009270 Review.
Cited by
-
ITO/poly(aniline)/sol-gel glass: An optically transparent, pH-responsive substrate for supported lipid bilayers.J Mater. 2013;2013:676920. doi: 10.1155/2013/676920. J Mater. 2013. PMID: 25328882 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity Comparison of Surface Plasmon Resonance and Plasmon-Waveguide Resonance Biosensors.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2011 Aug 10;156(1):169-175. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.04.008. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2011. PMID: 21666780 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmon Waveguide Resonance: Principles, Applications and Historical Perspectives on Instrument Development.Molecules. 2021 Oct 26;26(21):6442. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216442. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rabolt JF, Schlotter NE, Swalen JD. J Phys Chem. 1981;85:4141.
-
- Rabolt JF, Swalen JD. Structure and Orientation in Thin Films: Raman Studies with Integrated Optical Techniques. In: Clark RJH, Hester RE, editors. Spectroscopy of Surfaces. Chap 1 Wiley; Chichester: 1988.
-
- Saavedra SS, Reichert WM. Langmuir. 1991;7:995.
-
- Bohn PW. Prog Anal Spectrosc. 1989;12:41.
-
- Lukosz W. Sens Actuators, B. 1995;29:37.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

