Real-time monitoring of nuclear factor kappaB activity in cultured cells and in animal models
- PMID: 19796605
- PMCID: PMC2856067
Real-time monitoring of nuclear factor kappaB activity in cultured cells and in animal models
Abstract
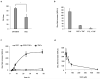
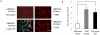
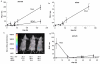
Nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) is a transcription factor that plays a major role in many human disorders, including immune diseases and cancer. We designed a reporter system based on NF-kappaB responsive promoter elements driving expression of the secreted Gaussia princeps luciferase (Gluc). We show that this bioluminescent reporter is a highly sensitive tool for noninvasive monitoring of the kinetics of NF-kappaB activation and inhibition over time, both in conditioned medium of cultured cells and in the blood and urine of animals. NF-kappaB activation was successfully monitored in real time in endothelial cells in response to tumor angiogenic signaling, as well as in monocytes in response to inflammation. Further, we demonstrated dual blood monitoring of both NF-kappaB activation during tumor development as correlated to tumor formation using the NF-kappaB Gluc reporter, as well as the secreted alkaline phosphatase reporter. This NF-kappaB reporter system provides a powerful tool for monitoring NF-kappaB activity in real time in vitro and in vivo.
Figures




References
-
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46:705–716. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2723–2735. - PubMed
-
- Pahl HL. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 1999;18:6853–6866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
