SynCAM1 recruits NMDA receptors via protein 4.1B
- PMID: 19796685
- PMCID: PMC2784006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.09.010
SynCAM1 recruits NMDA receptors via protein 4.1B
Abstract
Cell adhesion molecules have been implicated as key organizers of synaptic structures, but there is still a need to determine how these molecules facilitate neurotransmitter receptor recruitment to developing synapses. Here, we identify erythrocyte protein band 4.1-like 3 (protein 4.1B) as an intracellular effector molecule of Synaptic Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (SynCAM1) that is sufficient to recruit NMDA-type receptors (NMDARs) to SynCAM1 adhesion sites in COS7 cells. Protein 4.1B in conjunction with SynCAM1 also increased the frequency of NMDAR-mediated mEPSCs and area of presynaptic contact in an HEK293 cell/ neuron co-culture assay. Studies in cultured hippocampal neurons reveal that manipulation of protein 4.1B expression levels specifically affects NMDAR-mediated activity and localization. Finally, further experimentation in COS7 cells show that SynCAM1 may also interact with protein 4.1N to specifically effect AMPA type receptor (AMPAR) recruitment. Thus, SynCAM1 may recruit both AMPARs and NMDARs by independent mechanisms during synapse formation.
Figures
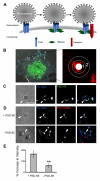
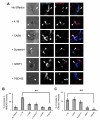
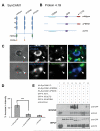
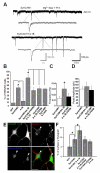
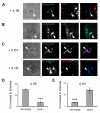
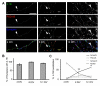
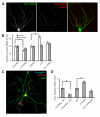
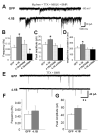
References
-
- An XL, Takakuwa Y, Nunomura W, Manno S, Mohandas N. Modulation of band 3-ankyrin interaction by protein 4.1. Functional implications in regulation of erythrocyte membrane mechanical properties. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:33187–33191. - PubMed
-
- Biederer T. Bioinformatic characterization of the SynCAM family of immunoglobulin-like domain-containing adhesion molecules. Genomics. 2005a - PubMed
-
- Biederer T. Progress from the postsynaptic side: signaling in synaptic differentiation. Sci STKE. 2005b;2005:pe9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

