The alpha(2)delta subunit augments functional expression and modifies the pharmacology of Ca(V)1.3 L-type channels
- PMID: 19796812
- PMCID: PMC7178495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.08.006
The alpha(2)delta subunit augments functional expression and modifies the pharmacology of Ca(V)1.3 L-type channels
Abstract
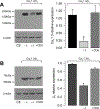
The auxiliary Ca(V)alpha(2)delta-1 subunit is an important component of voltage-gated Ca(2+) (Ca(V)) channel complexes in many tissues and of great interest as a drug target. Nevertheless, its exact role in specific cell functions is still unknown. This is particularly important in the case of the neuronal L-type Ca(V) channels where these proteins play a key role in the secretion of neurotransmitters and hormones, gene expression, and the activation of other ion channels. Therefore, using a combined approach of patch-clamp recordings and molecular biology, we studied the role of the Ca(V)alpha(2)delta-1 subunit on the functional expression and the pharmacology of recombinant L-type Ca(V)1.3 channels in HEK-293 cells. Co-expression of Ca(V)alpha(2)delta-1 significantly increased macroscopic currents and conferred the Ca(V)1.3alpha(1)/Ca(V)beta(3) channels sensitivity to the antiepileptic/analgesic drugs gabapentin and AdGABA. In contrast, Ca(V)alpha(2)delta-1 subunits harboring point mutations in N-glycosylation consensus sequences or the proteolytic site as well as in conserved cysteines in the transmembrane delta domain of the protein, reduced functionality in terms of enhancement of Ca(V)1.3alpha(1)/Ca(V)beta(3) currents. In addition, co-expression of the delta domain drastically inhibited macroscopic currents through recombinant Ca(V)1.3 channels possibly by affecting channel synthesis. Together these results provide several lines of evidence that the Ca(V)alpha(2)delta-1 auxiliary subunit may interact with Ca(V)1.3 channels and regulate their functional expression.
Figures
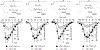


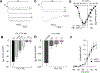



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of recombinant N-type and native high voltage-gated neuronal Ca2+ channels by AdGABA: mechanism of action studies.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Feb 1;250(3):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.10.030. Epub 2010 Nov 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21059371
-
Gabapentin-mediated inhibition of voltage-activated Ca2+ channel currents in cultured sensory neurones is dependent on culture conditions and channel subunit expression.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Mar;42(3):353-66. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(01)00181-2. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 11897114
-
Time course and specificity of the pharmacological disruption of the trafficking of voltage-gated calcium channels by gabapentin.Channels (Austin). 2008 Jan-Feb;2(1):4-9. doi: 10.4161/chan.2.1.6045. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Channels (Austin). 2008. PMID: 18690052
-
Functional biology of the alpha(2)delta subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007 May;28(5):220-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Apr 2. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17403543 Review.
-
The alpha2-delta protein: an auxiliary subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels as a recognized drug target.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Jul;11(7):761-70. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20571971 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the Ca2+ channel α2δ-1 auxiliary subunit in proliferation and migration of human glioblastoma cells.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 15;17(12):e0279186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279186. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36520928 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of Cavβ3 subunit in primary sensory neurons increases voltage-activated Ca2+ channel activity and nociceptive input in neuropathic pain.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):6002-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.310110. Epub 2011 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22187436 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and analysis of hub genes and networks related to hypoxia preconditioning in mice (No 035215).Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 21;9(15):11889-11904. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23555. eCollection 2018 Feb 23. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29552280 Free PMC article.
-
F0F1 ATP synthase regulates extracellular calcium influx in human neutrophils by interacting with Cav2.3 and modulates neutrophil accumulation in the lipopolysaccharide-challenged lung.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Feb 4;18(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-0515-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32019549 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of neuronal calcium channels.Neuronal Signal. 2017 Feb 20;1(1):NS20160003. doi: 10.1042/NS20160003. eCollection 2017 Feb. Neuronal Signal. 2017. PMID: 32714572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrade A, de Leon MB, Hernandez-Hernandez O, Cisneros B, Felix R, Myotonic dystrophy CTG repeat expansion alters Ca2+ channel functional expression in PC12 cells, FEBS Lett. 581 (2007) 4430–4438. - PubMed
-
- Avila T, Andrade A, Felix R, Transforming growth factor-b1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 downregulate CaV3.1 channel expression in mouse C2C12 myoblasts, J. Cell. Physiol 209 (2006) 448–456. - PubMed
-
- Bangalore R, Mehrke G, Gingrich K, Hofmann F, Kass RS Influence of L-type Ca channel α2/δ-subunit on ionic and gating current in transiently transfected HEK-293 cells, Am. J. Physiol 270 (1996) H1521–H1528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

