Requirement for the ERI/DICER complex in endogenous RNA interference and sperm development in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 19797044
- PMCID: PMC2787421
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.108134
Requirement for the ERI/DICER complex in endogenous RNA interference and sperm development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
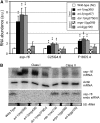
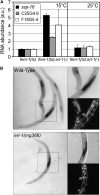
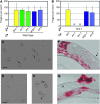
Small regulatory RNAs are key regulators of gene expression. One class of small regulatory RNAs, termed the endogenous small interfering RNAs (endo siRNAs), is thought to negatively regulate cellular transcripts via an RNA interference (RNAi)-like mechanism termed endogenous RNAi (endo RNAi). A complex of proteins composed of ERI-1/3/5, RRF-3, and DICER (the ERI/DICER complex) mediates endo RNAi processes in Caenorhabditis elegans. We conducted a genetic screen to identify additional components of the endo RNAi machinery. Our screen recovered alleles of eri-9, which encodes a novel DICER-interacting protein, and a missense mutation within the helicase domain of DICER [DCR-1(G492R)]. ERI-9(-) and DCR-1(G492) animals exhibit defects in endo siRNA expression and a concomitant failure to regulate mRNAs that exhibit sequence homology to these endo siRNAs, indicating that ERI-9 and the DCR-1 helicase domain function in the C. elegans endo RNAi pathway. We define a subset of Eri mutant animals (including eri-1, rrf-3, eri-3, and dcr-1, but not eri-9 or ergo-1) that exhibit temperature-sensitive, sperm-specific sterility and defects in X chromosome segregation. Among these mutants we find multiple aberrations in sperm development beginning with cytokinesis and extending through terminal differentiation. These results identify novel components of the endo RNAi machinery, demonstrate differential requirements for the Eri factors in the sperm-producing germline, and begin to delineate the functional requirement for the ERI/DICER complex in sperm development.
Figures




References
-
- Ambros, V., R. C. Lee, A. Lavanway, P. T. Williams and D. Jewell, 2003. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 13 807–818. - PubMed
-
- Asikainen, S., M. Storvik, M. Lakso and G. Wong, 2007. Whole genome microarray analysis of C. elegans rrf-3 and eri-1 mutants. FEBS Lett. 581 5050–5054. - PubMed
-
- Bühler, M., A. Verdel and D. Moazed, 2006. Tethering RITS to a nascent transcript initiates RNAi- and heterochromatin-dependent gene silencing. Cell 125 873–886. - PubMed
-
- Cam, H. P., T. Sugiyama, E. S. Chen, X. Chen, P. C. FitzGerald et al., 2005. Comprehensive analysis of heterochromatin- and RNAi-mediated epigenetic control of the fission yeast genome. Nat. Genet. 37 809–819. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

