Involvement of protein kinase C-CPI-17 in androgen modulation of angiotensin II-renal vasoconstriction
- PMID: 19797427
- PMCID: PMC2802204
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp326
Involvement of protein kinase C-CPI-17 in androgen modulation of angiotensin II-renal vasoconstriction
Abstract
Aims: Previous studies suggested that androgens augmented renal vascular responses to angiotensin II (Ang II). The protein kinase C (PKC)-CPI-17 pathway is involved in vascular constriction. We tested the hypothesis that this pathway may contribute to androgenic amplification of Ang II-renal vasoconstriction in the New Zealand genetically hypertensive (NZGH) rat.
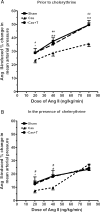
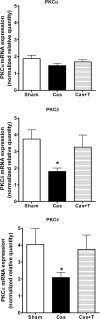
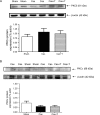
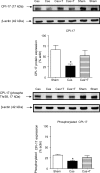
Methods and results: NZGH underwent sham operation, castration, or castration with testosterone replacement at 5 weeks of age. When the rats were 16-17 weeks of age, mean arterial pressure (MAP) and renal vascular resistance (RVR) responses to intravenous Ang II infusion (20, 40, and 80 ng/kg/min) were recorded before and after treatment with a PKC inhibitor, chelerythrine. mRNA expression of PKC isoforms and CPI-17 protein expression were analysed in renal cortex. MAP and RVR responses to Ang II were enhanced in androgen-replete NZGH. The Ang II-induced increase in RVR was significantly lower in castrated NZGH (ranged from 100 +/- 8% to 161 +/- 9% of baseline) than in sham-operated NZGH (ranged between 123 +/- 3% and 237 +/- 19% of baseline). Testosterone treatment restored RVR responses to Ang II in castrated rats. Chelerythrine treatment markedly reduced the MAP and RVR responses to Ang II in each group and attenuated the differential MAP and RVR responses to Ang II amongst the three groups. PKCdelta and PKCepsilon mRNA levels were significantly reduced by castration and increased by testosterone treatment. In contrast, no significant differences in protein expression were detected for these PKC isoforms. Castration decreased while testosterone treatment increased CPI-17 and phospho-CPI-17 expression.
Conclusion: Collectively, these results suggest that androgens modulate renal vascular responses to Ang II in part via an effect on the PKC-CPI-17 signalling pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Bazan E, Campbell AK, Rapoport RM. Protein kinase C activity in blood vessels from normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;227:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Crofton JT, Share L. Gonadal hormones modulate deoxycorticosterone-salt hypertension in male and female rats. Hypertension. 1997;29:494–499. - PubMed
-
- Dubey RK, Oparil S, Imthurn B, Jackson EK. Sex hormones and hypertension. Card Res. 2002;53:688–708. - PubMed
-
- Fortepiani LA, Reckelhoff JF. Treatment with tetrahydrobiopterin reduces blood pressure in male SHR by reducing testosterone synthesis. Am J Physiol. 2005;288:R733–R736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

