Correlations between BCL6 rearrangement and outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP or R-CHOP
- PMID: 19797725
- PMCID: PMC2805749
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.007203
Correlations between BCL6 rearrangement and outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP or R-CHOP
Abstract
Background: BCL6 gene rearrangement is the most frequent chromosomal abnormality in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, a malignancy characterized by genetic heterogeneity and wide variability in clinical outcome. The prognostic significance of BCL6 rearrangement has not been evaluated in the context of rituximab therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. We analyzed the effect of the BCL6 rearrangement on survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP and CHOP plus rituximab (R-CHOP).
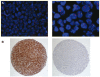
Design and methods: BCL6 rearrangement status was analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization with break-apart probes in 164 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP (n=65) or R-CHOP (n=99). Cell-of-origin immunophenotype including BCL6 protein expression were determined by immunohistochemistry on a tissue microarray.
Results: BCL6 rearrangement was detected in 19.5% of cases. The presence of the gene rearrangement was associated with a non-germinal center B-cell immunophenotype (P=0.006), and showed no correlation with BCL6 protein expression. A trend toward inferior overall survival was observed in association with the BCL6 rearrangement among patients treated with R-CHOP (P=0.08), but not among patients treated with CHOP (P=0.64). However, BCL6 rearrangement also correlated with a high International Prognostic Index score (P=0.02), and did not demonstrate independent prognostic value by multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: The introduction of rituximab may have altered the prognostic impact of BCL6 gene rearrangement in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. However, prospective analysis within large randomized clinical trials will be needed to clarify the prognostic significance of this biomarker in the rituximab era.
Figures
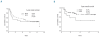
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008.
-
- Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Fermé C, et al. Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(18):4117–26. - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109(5):1857–61. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403(6769):503–11. - PubMed
-
- Lossos IS, Morgensztern D. Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(6):995–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

