The Scc2/Scc4 cohesin loader determines the distribution of cohesin on budding yeast chromosomes
- PMID: 19797771
- PMCID: PMC2758738
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1819409
The Scc2/Scc4 cohesin loader determines the distribution of cohesin on budding yeast chromosomes
Abstract
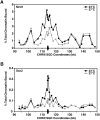
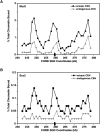
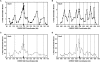
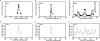
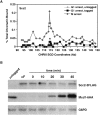
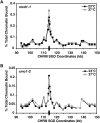
Cohesins mediate sister chromatid cohesion and DNA repair and also function in gene regulation. Chromosomal cohesins are distributed nonrandomly, and their deposition requires the heterodimeric Scc2/Scc4 loader. Whether Scc2/Scc4 establishes nonrandom cohesin distributions on chromosomes is poorly characterized, however. To better understand the spatial regulation of cohesin association, we mapped budding yeast Scc2 and Scc4 chromosomal distributions. We find that Scc2/Scc4 resides at previously mapped cohesin-associated regions (CARs) in pericentromeric and arm regions, and that Scc2/Scc4-cohesin colocalization persists after the initial deposition of cohesins in G1/S phase. Pericentromeric Scc2/Scc4 enrichment is kinetochore-dependent, and both Scc2/Scc4 and cohesin associations are coordinately reduced in these regions following chromosome biorientation. Thus, these characteristics of Scc2/Scc4 binding closely recapitulate those of cohesin. Although present in G1, Scc2/Scc4 initially has a poor affinity for CARs, but its affinity increases as cells traverse the cell cycle. Scc2/Scc4 association with CARs is independent of cohesin, however. Taken together, these observations are inconsistent with a previous suggestion that cohesins are relocated by translocating RNA polymerases from separate loading sites to intergenic regions between convergently transcribed genes. Rather, our findings suggest that budding yeast cohesins are targeted to CARs largely by Scc2/Scc4 loader association at these locations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mediator recruits the cohesin loader Scc2 to RNA Pol II-transcribed genes and promotes sister chromatid cohesion.Curr Biol. 2022 Jul 11;32(13):2884-2896.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.05.019. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35654035 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-specific cleavage of Scc2 regulates its cohesin deposition activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 13;111(19):7060-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321722111. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24778232 Free PMC article.
-
Structural evidence for Scc4-dependent localization of cohesin loading.Elife. 2015 Jun 3;4:e06057. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06057. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26038942 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into cohesin loading.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0723-6. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28631016 Review.
-
Condensin goes with the family but not with the flow.Genome Biol. 2008 Oct 6;9(10):236. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-10-236. Genome Biol. 2008. PMID: 18844972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fork pausing allows centromere DNA loop formation and kinetochore assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 13;115(46):11784-11789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806791115. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30373818 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of Cdc7 Protein Kinase During DNA Replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Nov 6;7(11):3757-3774. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300223. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28924058 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic reduction of cohesin differentially affects chromosome segregation, condensation, and DNA repair.Curr Biol. 2010 May 25;20(10):957-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.018. Epub 2010 May 6. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20451387 Free PMC article.
-
A streamlined cohesin apparatus is sufficient for mitosis and meiosis in the protist Tetrahymena.Chromosoma. 2018 Dec;127(4):421-435. doi: 10.1007/s00412-018-0673-x. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Chromosoma. 2018. PMID: 29948142 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin-dependent association of scc2/4 with the centromere initiates pericentromeric cohesion establishment.Curr Biol. 2013 Apr 8;23(7):599-606. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.02.022. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 23499533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arumugam P, Gruber S, Tanaka K, Haering CH, Mechtler K, Nasmyth K. ATP hydrolysis is required for cohesin's association with chromosomes. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shahar TR, Heeger S, Lehane C, East P, Flynn H, Skehel M, Uhlmann F. Eco1-dependent cohesin acetylation during establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Science. 2008;321:563–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
