Patient-reported-outcomes in subjects with painful lumbar or cervical radiculopathy treated with pregabalin: evidence from medical practice in primary care settings
- PMID: 19798503
- PMCID: PMC2877314
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-009-1086-1
Patient-reported-outcomes in subjects with painful lumbar or cervical radiculopathy treated with pregabalin: evidence from medical practice in primary care settings
Abstract
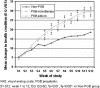
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of pregabalin in painful cervical or lumbosacral radiculopathy treated in Primary Care settings under routine clinical practice. An observational, prospective 12-week secondary analysis was carried-out. Male and female above 18 years, naïve to PGB, with refractory chronic pain secondary to cervical/lumbosacral radiculopathy were enrolled. SF-MPQ, Sheehan Disability Inventory, MOS Sleep Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the EQ-5D were administered. A total of 490 (34%) patients were prescribed PGB-monotherapy, 702 (48%) received PGB add-on, and 159 (11%) were administered non-PGB drugs. After 12 weeks, significant improvements in pain, associated symptoms of anxiety, depression and sleep disturbances, general health; and level of disability were observed in the three groups, being significantly greater in PGB groups. In routine medical practice, monotherapy or add-on pregabalin is associated with substantial pain alleviation and associated symptoms improvements in painful cervical or lumbosacral radiculopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
One of the authors of this study, Javier Rejas, is an employee of Pfizer Spain, which is the entity funding this project. Mª Teresa Saldaña, Ana Navarro, and Concepción Pérez have received honoraries from Pfizer Spain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A cost-consequences analysis of the effect of pregabalin in the treatment of painful radiculopathy under medical practice conditions in primary care settings.Pain Pract. 2010 Jan-Feb;10(1):31-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2009.00312.x. Pain Pract. 2010. PMID: 20629966 Clinical Trial.
-
A cost-consequences analysis of the effect of pregabalin in the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain in routine medical practice in primary care settings.BMC Neurol. 2011 Jan 20;11:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-11-7. BMC Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21251268 Free PMC article.
-
Pain alleviation and patient-reported health outcomes following switching to pregabalin in individuals with gabapentin-refractory neuropathic pain in routine medical practice.Clin Drug Investig. 2012 Jun 1;32(6):401-12. doi: 10.2165/11599400-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2012. PMID: 22480279
-
Pregabalin and gabapentin for the treatment of sciatica.J Clin Neurosci. 2016 Apr;26:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.05.061. Epub 2015 Nov 26. J Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26633090 Review.
-
The effect of pregabalin on pain-related sleep interference in diabetic peripheral neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia: a review of nine clinical trials.Curr Med Res Opin. 2010 Oct;26(10):2411-9. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2010.516142. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. PMID: 20812792 Review.
Cited by
-
Pregabalin for Refractory Radicular Leg Pain due to Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Preliminary Prospective Study.Pain Res Manag. 2016;2016:5079675. doi: 10.1155/2016/5079675. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Pain Res Manag. 2016. PMID: 27445615 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the responsiveness of four scales in geriatric patients with chronic neck pain.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Oct;41(10):1825-1831. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04957-6. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34302231 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Mirogabalin on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain due to Lumbar Spine Disease.Asian Spine J. 2021 Jun;15(3):349-356. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0136. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Asian Spine J. 2021. PMID: 32872751 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive drug safety evaluation of pregabalin in peripheral neuropathic pain.Pain Pract. 2015 Jan;15(1):47-57. doi: 10.1111/papr.12146. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Pain Pract. 2015. PMID: 24279736 Free PMC article.
-
Adding pregabalin or gabapentin for the management of community-treated patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a comparative cost analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2013 Nov;33(11):825-35. doi: 10.1007/s40261-013-0131-8. Clin Drug Investig. 2013. PMID: 24085589
References
-
- Lawrence RC, Helmick CG, Arnett FC, Deyo RA, Felson DT, Giannini EH, Heyse SP, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG, Liang MH, Pillemer SR, Steen VD, Wolfe F. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(5):778–799. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199805)41:5<778::AID-ART4>3.0.CO;2-V. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Donk J, Schouten JSAG, Passchier J, van Romunde LKJ, Valkenberg HA. The association of neck pain with radiological abnormalities of the cervical spine and personality traits in a general population. J Rheumatol. 1991;18:1884–1889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources