Alpha-tocopherol decreases iron-induced hippocampal and nigral neuron loss
- PMID: 19798567
- PMCID: PMC11498760
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9461-8
Alpha-tocopherol decreases iron-induced hippocampal and nigral neuron loss
Abstract
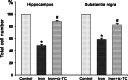
There are many studies about iron-induced neuronal hyperactivity and oxidative stress. Some reports also showed that iron levels rise in the brain in some neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). It has been suggested that excessive iron level increases oxidative stress and causes neuronal death. Tocopherols act as a free radical scavenger when phenoxylic head group encounters a free radical. We have aimed to identify the effect of alpha-tocopherol (Vitamin E) on iron-induced neurotoxicity. For this reason, rats were divided into three groups as control, iron, and iron + alpha-tocopherol groups. Iron chloride (200 mM in 2.5 microl volume) was injected into brain ventricle of iron and iron + alpha-tocopherol group rats. Same volume of saline (2.5 microl) was given to the rats belonging to control group. Rats of iron + alpha-tocopherol group received intraperitoneally (i.p.) alpha-tocopherol (100 mg/kg/day) for 10 days. After 10 days, rats were perfused intracardially under deep urethane anesthesia. Removed brains were processed using standard histological techniques. The numbers of neurons in hippocampus and substantia nigra of all rats were estimated by stereological techniques. Results of present study show that alpha-tocopherol decreased hippocampal and nigral neuron loss from 51.7 to 12.1% and 41.6 to 17.8%, respectively. Findings of the present study suggest that alpha-tocopherol may have neuroprotective effects against iron-induced hippocampal and nigral neurotoxicity and it may have a therapeutic significance for neurodegenerative diseases involved iron.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-treatment and post-treatment with alpha-tocopherol attenuates hippocampal neuronal damage in experimental cerebral hypoperfusion.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 1;571(2-3):120-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.048. Epub 2007 Jun 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17597609
-
Neuroprotection by 7-nitroindazole against iron-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Nov;27(7):933-41. doi: 10.1007/s10571-007-9223-4. Epub 2007 Oct 27. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17965933 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking of L-type calcium channels protects hippocampal and nigral neurons against iron neurotoxicity. The role of L-type calcium channels in iron-induced neurotoxicity.Int J Neurosci. 2013 Dec;123(12):876-82. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.813510. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Int J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23768064
-
Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Dec;345(1-2):91-104. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0563-x. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20730621 Review.
-
Multifunctional activities of green tea catechins in neuroprotection. Modulation of cell survival genes, iron-dependent oxidative stress and PKC signaling pathway.Neurosignals. 2005;14(1-2):46-60. doi: 10.1159/000085385. Neurosignals. 2005. PMID: 15956814 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics-based identification of metabolic alterations in PARK2.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019 Feb 21;6(3):525-536. doi: 10.1002/acn3.724. eCollection 2019 Mar. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30911576 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E and Its Molecular Effects in Experimental Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 7;24(13):11191. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311191. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of apoptotic change in the rat hippocampus caused by ferric nitrilotriacetate.Redox Rep. 2011;16(3):114-20. doi: 10.1179/174329211X13049558293597. Redox Rep. 2011. PMID: 21801493 Free PMC article.
-
Iron and Targeted Iron Therapy in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 15;24(22):16353. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216353. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain tocopherols related to Alzheimer's disease neuropathology in humans.Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jan;11(1):32-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.12.015. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 24589434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amoroso S, Gioielli A, Cataldi M, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (1999) In the neuronal cell line SH-SY5Y, oxidative stress-induced free radical overproduction causes cell death without any participation of intracellular Ca2+ increase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1452:151–160 - PubMed
-
- Behl C, Davis J, Cole GM, Schubert D (1992) Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid h protein toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186:944–950 - PubMed
-
- Bondy SC, Guo S, Adams JD (1996) Prevention of ethanol-induced changes in reactive oxygen parameters by alpha-tocopherol. Alcohol Alcohol 31:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Bostanci MO, Bagirici F (2008) Nitric oxide synthesis inhibition attenuates iron-induced neurotoxicity: a stereological study. Neurotoxicology 29(1):130–135 - PubMed
-
- Bostanci MO, Bagirici F, Canan S (2006) A calcium channel blocker flunarizine attenuates the neurotoxic effects of iron. Cell Biol Toxicol 22:119–125 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical