The use of nanoparticle-mediated targeted gene silencing and drug delivery to overcome tumor drug resistance
- PMID: 19800114
- PMCID: PMC2783414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.048
The use of nanoparticle-mediated targeted gene silencing and drug delivery to overcome tumor drug resistance
Abstract
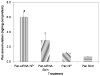
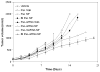
Overexpression of drug efflux transporters such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp) enables cancer cells to develop resistance to multiple anticancer drugs. Functional inhibitors of P-gp have shown promising efficacy in early clinical trials, but their long-term safety is yet to be established. A novel approach to overcome drug resistance is to use siRNA-mediated RNA interference to silence the expression of the efflux transporter. Because P-gp plays an important role in the physiological regulation of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds in the body, it is important to deliver P-gp targeted siRNA and anticancer drug specifically to tumor cells. Further, for optimal synergy, both the drug and siRNA may need to be temporally colocalized in the tumor cells. In the current study, we investigated the effectiveness of simultaneous and targeted delivery of anticancer drug, paclitaxel, along with P-gp targeted siRNA, using poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles to overcome tumor drug resistance. Nanoparticles were surface functionalized with biotin for active tumor targeting. Dual agent nanoparticles encapsulating the combination of paclitaxel and P-gp targeted siRNA showed significantly higher cytotoxicity in vitro than nanoparticles loaded with paclitaxel alone. Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of dual agent nanoparticles could be correlated with effective silencing of the MDR1 gene that encodes for P-gp and with increased accumulation of paclitaxel in drug-resistant tumor cells. In vivo studies in a mouse model of drug-resistant tumor demonstrated significantly greater inhibition of tumor growth following treatment with biotin-functionalized nanoparticles encapsulating both paclitaxel and P-gp targeted siRNA at a paclitaxel dose that was ineffective in the absence of gene silencing. These results suggest that that the combination of P-gp gene silencing and cytotoxic drug delivery using targeted nanoparticles can overcome tumor drug resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-mediated simultaneous and targeted delivery of paclitaxel and tariquidar overcomes tumor drug resistance.J Control Release. 2009 May 21;136(1):21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.01.021. Epub 2009 Feb 5. J Control Release. 2009. PMID: 19331851
-
Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by CD44 antibody-targeted nanocomplexes for short hairpin RNA-encoding plasmid DNA delivery.Biomaterials. 2015 Mar;45:99-114. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.12.030. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25662500
-
Folic Acid-Modified Nanoerythrocyte for Codelivery of Paclitaxel and Tariquidar to Overcome Breast Cancer Multidrug Resistance.Mol Pharm. 2020 Apr 6;17(4):1114-1126. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01148. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32176509
-
P-glycoprotein inhibition as a therapeutic approach for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: current status and future perspectives.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Mar;13(3):326-46. doi: 10.2174/15680096113139990076. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23369096 Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies to overcome taxane resistance in cancer.Drug Resist Updat. 2021 Mar;55:100754. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2021.100754. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Drug Resist Updat. 2021. PMID: 33691261 Review.
Cited by
-
Concepts and practices used to develop functional PLGA-based nanoparticulate systems.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:747-65. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S40579. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23459088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-delivery of siRNA and therapeutic agents using nanocarriers to overcome cancer resistance.Nano Today. 2012 Aug 1;7(4):367-379. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2012.06.013. Nano Today. 2012. PMID: 26257819 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired tumor-homing nanoplatform for co-delivery of paclitaxel and siRNA-E7 to HPV-related cervical malignancies for synergistic therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(7):3325-3339. doi: 10.7150/thno.41228. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194871 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle delivery of antisense oligonucleotides and their application in the exon skipping strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014 Feb;24(1):87-100. doi: 10.1089/nat.2013.0450. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014. PMID: 24506782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of nanomaterials and biological systems: Implications to personalized nanomedicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Oct;64(13):1363-84. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22917779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Teicher BA. Acute and chronic in vivo therapeutic resistance. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:1665–73. - PubMed
-
- Duhem C, Ries F, Dicato M. What Does Multidrug Resistance (MDR) Expression Mean in the Clinic? Oncologist. 1996;1:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Clarke R, Leonessa F, Trock B. Multidrug resistance/P-glycoprotein and breast cancer: review and meta-analysis. Semin Oncol. 2005;32:S9–15. - PubMed
-
- Patil Y, Sadhukha T, Ma L, Panyam J. Nanoparticle-mediated simultaneous and targeted delivery of paclitaxel and tariquidar overcomes tumor drug resistance. J Control Release. 2009;136:21–9. - PubMed
-
- Soma CE, Dubernet C, Bentolila D, Benita S, Couvreur P. Reversion of multidrug resistance by co-encapsulation of doxorubicin and cyclosporin A in polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

