Tyrosines in the kinesin-5 head domain are necessary for phosphorylation by Wee1 and for mitotic spindle integrity
- PMID: 19800237
- PMCID: PMC2762001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.08.013
Tyrosines in the kinesin-5 head domain are necessary for phosphorylation by Wee1 and for mitotic spindle integrity
Abstract
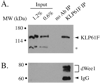
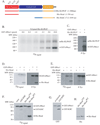
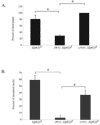
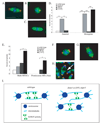
Mitotic spindle assembly and maintenance relies on kinesin-5 motors that act as bipolar homotetramers to crosslink microtubules. Kinesin-5 motors have been the subject of extensive structure-function analysis, but the regulation of their activity in the context of mitotic progression remains less well understood. We report here that Drosophila kinesin-5 (KLP61F) is regulated by Drosophila Wee1 (dWee1). Wee1 tyrosine kinases are known to regulate mitotic entry via inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdk1. Recently, we showed that dWee1 also plays a role in mitotic spindle positioning through gamma-tubulin and spindle fidelity through an unknown mechanism. Here, we investigated whether a KLP61F-dWee1 interaction could explain the latter role of dWee1. We found that dWee1 phosphorylates KLP61F in vitro on three tyrosines within the head domain, the catalytic region that mediates movement along microtubules. In vivo, KLP61F with tyrosine-->phenylalanine mutations fails to complement a klp61f mutant and dominantly induces spindle defects similar to ones seen in dwee1 mutants. We propose that phosphorylation of the KLP61F catalytic domain by dWee1 is important for the motor's function. This study identifies a second substrate for a Wee1 kinase and provides evidence for phosphoregulation of a kinesin in the head domain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila Wee1 interacts with members of the gammaTURC and is required for proper mitotic-spindle morphogenesis and positioning.Curr Biol. 2005 Sep 6;15(17):1525-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.031. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16139207 Free PMC article.
-
The bipolar kinesin, KLP61F, cross-links microtubules within interpolar microtubule bundles of Drosophila embryonic mitotic spindles.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jan 11;144(1):125-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.1.125. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9885249 Free PMC article.
-
Mitosis: KLP61F goes wee!Curr Biol. 2009 Oct 13;19(19):R899-901. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.003. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19825352
-
Regulation of Aurora-A kinase on the mitotic spindle.Chromosoma. 2003 Dec;112(4):159-63. doi: 10.1007/s00412-003-0265-1. Epub 2003 Nov 21. Chromosoma. 2003. PMID: 14634755 Review.
-
Mitotic functions of kinesin-5.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 May;21(3):255-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.019. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20109572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinesin-5: cross-bridging mechanism to targeted clinical therapy.Gene. 2013 Dec 1;531(2):133-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23954229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila Xpd regulates Cdk7 localization, mitotic kinase activity, spindle dynamics, and chromosome segregation.PLoS Genet. 2010 Mar 12;6(3):e1000876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000876. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20300654 Free PMC article.
-
Src family kinase phosphorylation of the motor domain of the human kinesin-5, Eg5.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2017 Sep;74(9):317-330. doi: 10.1002/cm.21380. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 28646493 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Expression Profiling and Phenotypic Analysis of Downstream Targets Identify the Fox Transcription Factor Jumeau as a Master Regulator of Cardiac Progenitor Cell Division.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 1;25(23):12933. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312933. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684645 Free PMC article.
-
Three Cdk1 sites in the kinesin-5 Cin8 catalytic domain coordinate motor localization and activity during anaphase.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3395-3412. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2523-z. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28455557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kashina AS, Rogers GC, Scholey JM. The bimC family of kinesins: essential bipolar mitotic motors driving centrosome separation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1357:257–271. - PubMed
-
- Tao L, Mogilner A, Civelekoglu-Scholey G, Wollman R, Evans J, Stahlberg H, Scholey JM. A homotetrameric kinesin-5, KLP61F, bundles microtubules and antagonizes Ncd in motility assays. Curr Biol. 2006;16:2293–2302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

