Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus tapeworms in China as determined by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences
- PMID: 19800346
- PMCID: PMC2823955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.09.006
Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus tapeworms in China as determined by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences
Abstract
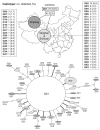
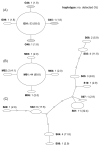
The genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus spp. in the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region were evaluated by DNA sequencing analyses of genes for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (cox1) and nuclear elongation factor-1 alpha (ef1a). We collected 68 isolates of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (s.s.) from Xinjiang and 113 isolates of E. granulosus s. s., 49 isolates of Echinococcus multilocularis and 34 isolates of Echinococcus shiquicus from the Tibetan Plateau. The results of molecular identification by mitochondrial and nuclear markers were identical, suggesting the infrequency of introgressive hybridization. A considerable intraspecific variation was detected in mitochondrial cox1 sequences. The parsimonious network of cox1 haplotypes showed star-like features in E. granulosus s. s. and E. multilocularis, but a divergent feature in E. shiquicus. The cox1 neutrality indexes computed by Tajima's D and Fu's Fs tests showed high negative values in E. granulosus s. s. and E. multilocularis, indicating significant deviations from neutrality. In contrast, the low positive values of both tests were obtained in E. shiquicus. These results suggest the following hypotheses: (i) recent founder effects arose in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis after introducing particular individuals into the endemic areas by anthropogenic movement or natural migration of host mammals, and (ii) the ancestor of E. shiquicus was segregated into the Tibetan Plateau by colonising alpine mammals and its mitochondrial locus has evolved without bottleneck effects.
2009 Australian Society for Parasitology Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bart JM, Abdukader M, Zhang YL, Lin RY, Wang YH, Nakao M, Ito A, Craig PS, Piarroux R, Vuitton DA, Wen H. Genotyping of human cystic echinococcosis in Xinjiang, PR China. Parasitology. 2006;133:571–579. - PubMed
-
- Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992;54:165–173. - PubMed
-
- Budke CM, Jiamin Q, Qian W, Torgerson PR. Economic effects of echinococcosis in a disease-endemic region of the Tibetan Plateau. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005;73:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Chen SY, Duan ZY, Sha T, Xiangyu J, Wu SF, Zhang YP. Origin, genetic diversity, and population structure of Chinese domestic sheep. Gene. 2006;376:216–223. - PubMed
-
- Clement M, Posada D, Crandall K. TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000;9:1657–1660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

